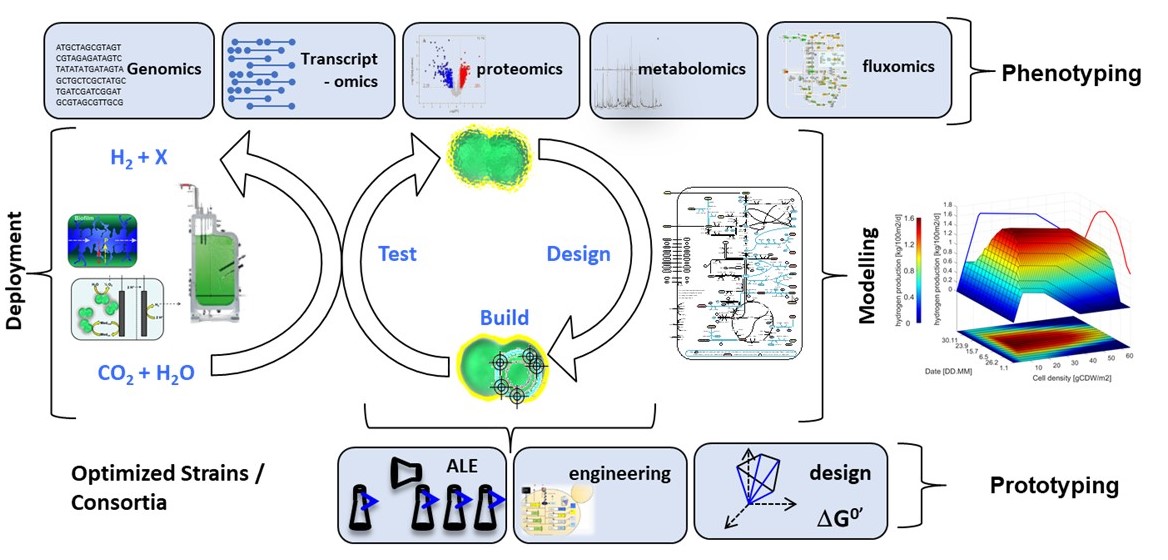
Research Focus:
The research group Systems Biotechnology works in the core areas quantitative physiology and manipulation of redox balances with the overall aim of the sustainable production of chemicals and green energy carriers such as H2. We focus on several key classes of organisms: On the one hand we use photoautotrophic cyanobacteria (farmers) to provide redox power and organic carbon, on the other hand we employ metabolically engineered microbes (including heterotrophs) as production organisms (laborers). A third type of cell might come into play to stabilize synthetic consortia (balancers). We use pure cultures, co-cultures and synthetic consortia to achieve our goals for production. Applying Systems Metabolic Engineering to individual cell types following an iterative design-build-test-learn cycle, is a key approach to achieve our aims.
As a consequence, the group rests on four main pillars: (i) Modelling of metabolism (including metabolic flux analysis and genome scale modelling), (ii) analytics (metabolite fingerprinting, quantification, and isotope enrichments), (iii) in-depth physiology using mass-balanced culture techniques and ‘omics characterization, and last but not least (iv) microbial electrochemical technologies (MET) which allows the reversible conversion of electrical energy into biochemical energy to steer metabolism at the push of a button.
To address the diverse needs of the four pillars, the staff is organized in interdisciplinary research teams with a special focus on certain aspects of the pillars.
Group Leader:
Academic Staff:
Dr. Fabian Brandenburg
Hans Schneider
Dr. Chandrakant Joshi
Caroline Ruhl
PhD-Students:
Jianqi Yuan (jointly with BPV group)
Technician:
Philip Haus
Guest Researchers:
Patrícia Verardi Abdelnur, DSc
Index:
You could use our publication index for further requests.
2026 (2)
- Kas, A., Izadi, P., Lenz, C., Rohwerder, T., Krömer, J.O., Harnisch, F. (2026):
Exploring ectoine production from methanol, formate, and electrochemically produced formate by Methyloligella halotolerans
Eng. Life Sci. 26 (1), e70063 10.1002/elsc.70063 - Yuan, J., Lai, B., Krömer, J.O. (2026):
Comparative effects of monochromatic red and broad-spectrum white light on biophotovoltaics: Stability, efficiency, and application potential
Bioelectrochemistry 168 , art. 109164 10.1016/j.bioelechem.2025.109164
2025 (8)
- Pan, M., Amarante Colpo, R., Roussou, S., Ding, C., Lindblad, P., Krömer, J.O. (2025):
Engineering a photoautotrophic microbial coculture toward enhanced biohydrogen production
Environ. Sci. Technol. 59 (1), 337 - 348 10.1021/acs.est.4c08629 - Pan, M., Krömer, J.O. (2025):
Phototrophe Konsortien für nachhaltige Energie und Stoffkreisläufe
Biospektrum 31 , 764 - 766 10.1007/s12268-025-2624-4 - Resch, M.G., Badgett, A., Krömer, J.O., Marcellin, E. (2025):
Upstream considerations for gas fermentation processes
Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 95 , art. 103337 10.1016/j.copbio.2025.103337 - Roussou, S., Pan, M., Krömer, J.O., Lindblad, P. (2025):
Exploring and increased acetate biosynthesis in Synechocystis PCC 6803 through insertion of a heterologous phosphoketolase and overexpressing phosphotransacetylase
Metab. Eng. 88 , 250 - 260 10.1016/j.ymben.2025.01.008 - Schneider, H., Lai, B., Krömer, J.O. (2025):
Understanding the electron pathway fluidity of Synechocystis in biophotovoltaics
Plant J. 121 (2), e17225 10.1111/tpj.17225 - Weimer, A., Krömer, J., Lai, B., Wittmann, C. (2025):
The TonB-dependent transport system facilitates the uptake of inorganic metal mediators in Pseudomonas putida KT2440 in a bioelectrochemical system
Microb. Biotechnol. 18 (8), e70206 10.1111/1751-7915.70206 - Yuan, J., Appel, J., Gutekunst, K., Lai, B., Krömer, J.O. (2025):
Molecular dynamics of photosynthetic electron flow in a biophotovoltaic system
Environ. Sci. Ecotechnol. 23 , art. 100519 10.1016/j.ese.2024.100519 - Yuan, J., Bai, Y., Lenz, C., Reilly-Schott, V., Schneider, H., Lai, B., Krömer, J.O. (2025):
The impact of redox mediators on the electrogenic and physiological properties of Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 in a biophotovoltaic system
ChemSusChem 18 (13), e202402543 10.1002/cssc.202402543
2024 (2)
- Pause, L., Weimer, A., Wirth, N.T., Nguyen, A.V., Lenz, C., Kohlstedt, M., Wittmann, C., Nikel, P.I., Lai, B., Krömer, J.O. (2024):
Anaerobic glucose uptake in Pseudomonas putida KT2440 in a bioelectrochemical system
Microb. Biotechnol. 17 (1), e14375 10.1111/1751-7915.14375 - Weimer, A., Pause, L., Ries, F., Kohlstedt, M., Adrian, L., Krömer, J., Lai, B., Wittmann, C. (2024):
Systems biology of electrogenic Pseudomonas putida - multi-omics insights and metabolic engineering for enhanced 2-ketogluconate production
Microb. Cell. Fact. 23 , art. 246 10.1186/s12934-024-02509-8
2023 (4)
- Lai, B., Krömer, J., Aulenta, F., Wu, H., Nikel, P.I. (2023):
Exploiting synergies between microbial electrochemical technologies and synthetic biology
Microb. Biotechnol. 16 (3), 485 - 488 10.1111/1751-7915.14208 - Pan, M., Wang, Y., Krömer, J.O., Zhu, X., Lin, M.K.T.H., Angelidaki, I. (2023):
A coculture of photoautotrophs and hydrolytic heterotrophs enables efficient upcycling of starch from wastewater toward biomass-derived products: Synergistic interactions impacting metabolism of the consortium
Environ. Sci. Technol. 57 (41), 15523 - 15532 10.1021/acs.est.3c05321 - Schneider, H., Lai, B., Krömer, J. (2023):
Interference of electron transfer chain inhibitors in bioelectrochemical systems
Electrochem. Commun. 152 , art. 107527 10.1016/j.elecom.2023.107527 - Schneider, H., Lai, B., Krömer, J. (2023):
Utilizing cyanobacteria in biophotovoltaics: An emerging field in bioelectrochemistry
In: Bühler, K., Lindberg, P. (eds.)
Cyanobacteria in biotechnology. Applications and quantitative perspectives
Adv. Biochem. Eng. Biotechnol. 183
Springer Nature, p. 281 - 302 10.1007/10_2022_212
2022 (3)
- Brandenburg, F., Klähn, S., Schmid, A., Krömer, J.O. (2022):
Produktion von Aminosäurederivaten in Cyanobakterien [Production of amino acid derivatives in cyanobacteria]
Biospektrum 28 (3), 341 - 343 10.1007/s12268-022-1756-z - Gemünde, A., Lai, B., Pause, L., Krömer, J., Holtmann, D. (2022):
Redox mediators in microbial electrochemical systems
ChemElectroChem 9 (13), e202200216 10.1002/celc.202200216 - Plan, M., Bongers, M., Bydder, S., Fabris, M., Hodson, M.P., Kelly, E., Krömer, J., Perez-Gil, J., Peng, B., Satta, A., Schrübbers, L.C., Vickers, C.E. (2022):
Analysing intracellular isoprenoid metabolites in diverse prokaryotic and eukaryotic microbes
In: Wurtzel, E.T. (ed.)
Carotenoids: Carotenoid and apocarotenoid analysis
Methods Enzymol. 670
Elsevier, p. 235 - 284 10.1016/bs.mie.2022.03.018
2021 (8)
- Brandenburg, F., Theodosiou, E., Bertelmann, C., Grund, M., Klähn, S., Schmid, A., Krömer, J.O. (2021):
Trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline production by the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803
Metab. Eng. Commun. 12 , e00155 10.1016/j.mec.2020.e00155 - Bühler, K., Bühler, B., Klähn, S., Krömer, J.O., Dusny, C., Schmid, A. (2021):
Biocatalytic production of white hydrogen from water using cyanobacteria
In: Rögner, M. (ed.)
Photosynthesis: Biotechnological applications with microalgae
De Gruyter, Berlin ; Boston, p. 279 - 306 10.1515/9783110716979-011 - Bühler, K., Krömer, J.O., Klähn, S., Bühler, B., Dusny, C., Schmid, A. (2021):
Weißer Wasserstoff made in Leipzig [White hydrogen made in Leipzig]
Biospektrum 27 (3), 335 10.1007/s12268-021-1572-x - Krömer, J.O. (2021):
Buchrezension zu: Industrial Microbiology
Biospektrum 27 (4), 452 10.1007/s12268-021-1581-9 - Lai, B., Schneider, H., Tschörtner, J., Schmid, A., Krömer, J.O. (2021):
Inside front cover image, Volume 118, Number 7, July 2021
Biotechnol. Bioeng. 118 (7), ii - ii 10.1002/bit.27411 - Lai, B., Schneider, H., Tschörtner, J., Schmid, A., Krömer, J.O. (2021):
Technical-scale biophotovoltaics for long-term photo-current generation from Synechocystis sp. PCC6803
Biotechnol. Bioeng. 118 (7), 2637 - 2648 10.1002/bit.27784 - Nguyen, A.V., Lai, B., Adrian, L., Krömer, J.O. (2021):
The anoxic electrode-driven fructose catabolism of Pseudomonas putida KT2440
Microb. Biotechnol. 14 (4), 1784 - 1796 10.1111/1751-7915.13862 - Welter, E.S., Kött, S., Brandenburg, F., Krömer, J.O., Goepel, M., Schmid, A., Gläser, R. (2021):
Figures of merit for photocatalysis: Comparison of NiO/La-NaTaO3 and Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 as a semiconductor and a bio-photocatalyst for water splitting
Catalysts 11 (11), art. 1415 10.3390/catal11111415
2020 (4)
- Babel, H., Krömer, J.O. (2020):
Evolutionary engineering of E. coli MG1655 for tolerance against isoprenol
Biotechnol. Biofuels 13 , art. 183 10.1186/s13068-020-01825-6 - Krömer, J.O., Ferreira, R.G., Petrides, D., Kohlheb, N. (2020):
Economic process evaluation and environmental life-cycle assessment of bio-aromatics production
Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 8 , art. 403 10.3389/fbioe.2020.00403 - Lai, B., Bernhardt, P.V., Krömer, J.O. (2020):
Cytochrome c reductase is a key enzyme involved in the extracellular electron transfer pathway towards transition metal complexes in Pseudomonas putida
ChemSusChem 13 (19), 5308 - 5317 10.1002/cssc.202001645 - Lai, B., Krömer, J.O. (2020):
Steering redox metabolism in Pseudomonas putida with microbial electrochemical technologies
In: Tiquia-Arashiro, S.M., Pant, D. (eds.)
Microbial Electrochemical Technologies
CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, p. 59 - 75 10.1201/9780429487118
2019 (3)
- Lai, B., Nguyen, A.V., Krömer, J.O. (2019):
Characterizing the anoxic phenotype of Pseudomonas putida using a bioelectrochemical system
Methods Protoc. 2 (2), art. 26 10.3390/mps2020026 - Tschörtner, J., Lai, B., Krömer, J.O. (2019):
Biophotovoltaics: green power generation from sunlight and water
Front. Microbiol. 10 , art. 866 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00866 - Vassilev, I., Kracke, F., Freguia, S., Keller, J., Krömer, J.O., Ledezma, P., Virdis, B. (2019):
Microbial electrosynthesis system with dual biocathode arrangement for simultaneous acetogenesis, solventogenesis and carbon chain elongation
Chem. Commun. 55 (30), 4351 - 4354 10.1039/c9cc00208a
2018 (8)
- Averesch, N.J.H., Krömer, J.O. (2018):
Metabolic engineering of the shikimate pathway for production of aromatics and derived compounds – present and future strain construction strategies
Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 6 , art. 32 10.3389/fbioe.2018.00032 - Averesch, N.J.H., Martínez, V.S., Nielsen, L.K., Krömer, J.O. (2018):
Toward synthetic biology strategies for adipic acid production: An in silico tool for combined thermodynamics and stoichiometric analysis of metabolic networks
ACS Synth. Biol. 7 (2), 490 - 509 10.1021/acssynbio.7b00304 - Kracke, F., Lai, B., Yu, S., Krömer, J.O. (2018):
Balancing cellular redox metabolism in microbial electrosynthesis and electro fermentation – A chance for metabolic engineering
Metab. Eng. 45 , 109 - 120 10.1016/j.ymben.2017.12.003 - Krieg, T., Phan, L.M.P., Wood, J.A., Sydow, A., Vassilev, I., Krömer, J.O., Mangold, K.-M., Holtmann, D. (2018):
Characterization of a membrane-separated and a membrane-less electrobioreactor for bioelectrochemical syntheses
Biotechnol. Bioeng. 115 (7), 1705 - 1716 10.1002/bit.26600 - Varela, C., Schmidt, S.A., Borneman, A.R., Pang, C.N.I., Krömer, J.O., Khan, A., Song, X., Hodson, M.P., Solomon, M., Mayr, C.M., Hines, W., Pretorius, I.S., Baker, M.S., Roessner, U., Mercurio, M., Henschke, P.A., Wilkins, M.R., Chambers, P.J. (2018):
Systems-based approaches enable identification of gene targets which improve the flavour profile of low-ethanol wine yeast strains
Metab. Eng. 49 , 178 - 191 10.1016/j.ymben.2018.08.006 - Vassilev, I., Gießelmann, G., Schwechheimer, S.K., Wittmann, C., Virdis, B., Krömer, J.O. (2018):
Anodic electro-fermentation: Anaerobic production of L-Lysine by recombinant Corynebacterium glutamicum
Biotechnol. Bioeng. 115 (6), 1499 - 1508 10.1002/bit.26562 - Vassilev, I., Hernandez, P.A., Batlle-Vilanova, P., Freguia, S., Krömer, J.O., Keller, J., Ledezma, P., Virdis, B. (2018):
Microbial electrosynthesis of isobutyric, butyric, caproic acids, and corresponding alcohols from carbon dioxide
ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 6 (7), 8485 - 8493 10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b00739 - Yu, S., Lai, B., Plan, M.R., Hodson, M.P., Lestari, E.A., Song, H., Krömer, J.O. (2018):
Improved performance of Pseudomonas putida in a bioelectrochemical system through overexpression of periplasmic glucose dehydrogenase
Biotechnol. Bioeng. 115 (1), 145 - 155 10.1002/bit.26433
2017 (4)
- Averesch, N.J.H., Prima, A., Krömer, J.O. (2017):
Enhanced production of para-hydroxybenzoic acid by genetically engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Bioprocess. Biosyst. Eng. 40 (8), 1283 - 1289 10.1007/s00449-017-1785-z - Gold, D.A., O'Reilly, S.S., Watson, J., Degnan, B.M., Degnan, S.M., Krömer, J.O., Summons, R.E. (2017):
Lipidomics of the sea sponge Amphimedon queenslandica and implication for biomarker geochemistry
Geobiology 15 (6), 836 - 843 10.1111/gbi.12253 - Koch, C., Kuchenbuch, A., Kracke, F., Bernhardt, P.V., Krömer, J.O., Harnisch, F. (2017):
Predicting and experimental evaluating bio-electrochemical synthesis — A case study with Clostridium kluyveri
Bioelectrochemistry 118 , 114 - 122 10.1016/j.bioelechem.2017.07.009 - Watson, J.R., Krömer, J.O., Degnan, B.M., Degnan, S.M. (2017):
Seasonal changes in environmental nutrient availability and biomass composition in a coral reef sponge
Mar. Biol. 164 (6), art. 135 10.1007/s00227-017-3167-0
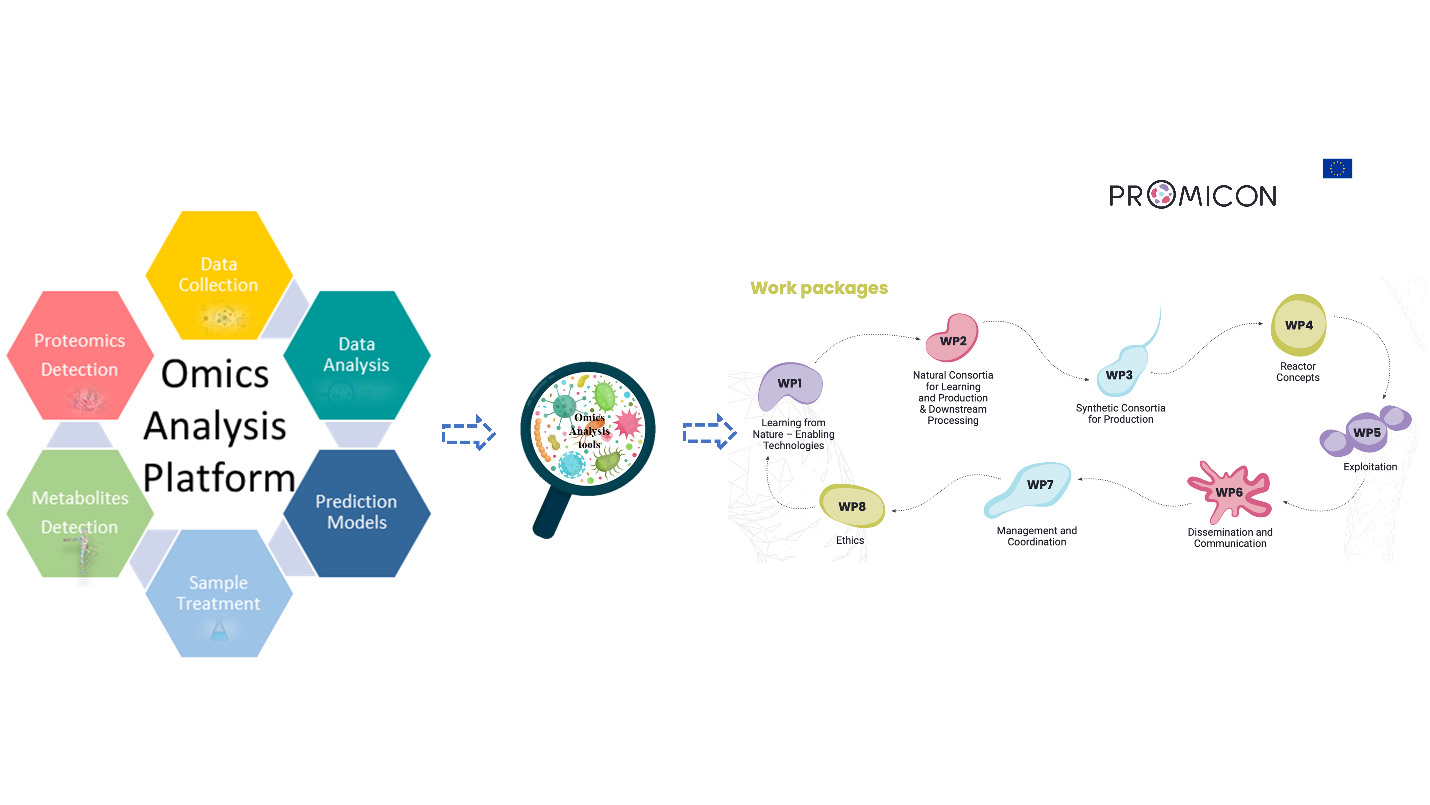
The PROMICON project
The deliberate control of complex microbiomes is notoriously difficult and current approaches are often guided by simple trial-and-error. Advances in quantitative analysis modeling and design of these systems are urgently needed to improve the predictability and enable the exploitation of the amazing synthesis capacities of microbiomes.
The PROMICON project will learn from nature how microbiomes function through development and application of quantitative physiology, imaging, cell sorting machine learning and systems biology. This will steer existing microbiomes towards production and generate new synthetic microbiomes inspired by nature through an iterative design-build-test-learn cycle. The new consortia will also contain strains developed through systems metabolic engineering and will be used for the production of energy carriers, drop-in chemical feedstocks and advanced biomaterials.
Our research group specializes in developing an integrated omics platform that encompasses metabolomics and proteomics measurements and analyses for both synthetic and natural microbial consortia. This approach aims to uncover complex microbial interactions and mechanisms, paving the way for the creation of highly productive microbial communities. PROMICON Webpage

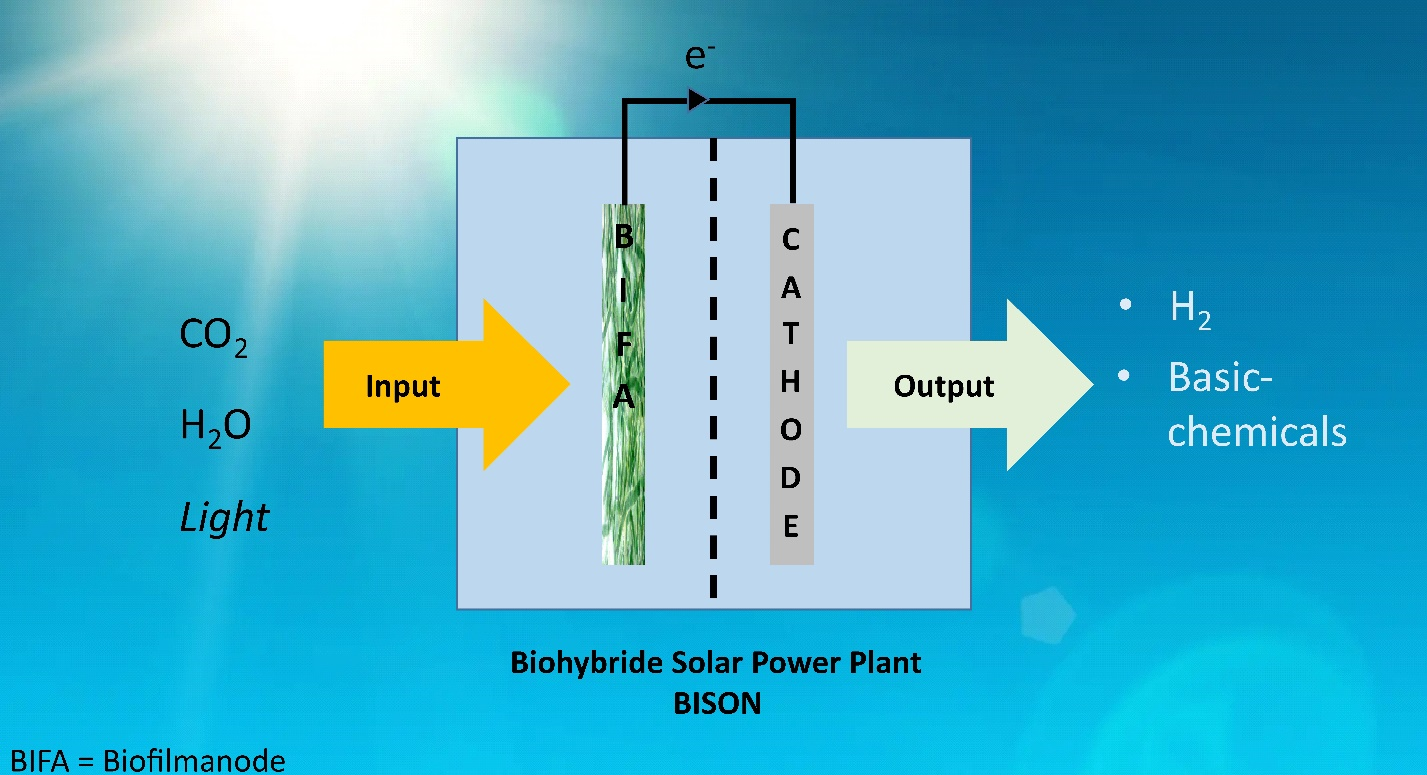
The BISON project
Biophotovoltaics (BPV) utilizes photosynthetic microorganisms to convert sunlight, water, and CO₂ into clean energy and valuable chemicals. However, optimizing the interaction between biological and electrochemical components in BPV systems is a significant challenge, requiring precise control and advanced analytical approaches.
The BISON project seeks to bridge this gap by combining cutting-edge bioelectrochemistry, material science, and systems biology. By understanding and enhancing the processes that drive BPV systems, the project aims to scale this innovative technology for real-world applications, enabling sustainable hydrogen production and CO₂ utilization.
In work package 3 (WP3) our group, uses quantitative bioanalysis and systems modeling to analyze which reactor settings, mediator-cell interactions or species work best. Thus, WP3 serves a central role in BISON, using metabolomics, proteomics, and advanced bioelectrochemical techniques to unravel the complex effects of electron flow on photosynthetic microorganisms. This integrated approach ensures the stability and productivity of BPV systems, paving the way for scalable, renewable energy solutions.

New concepts for an integrative bio economy: Sustainable Valorization of CO2 and sunlight
This project aims to generate a sustainable resource platform on the basis of CO2 driven by light energy from sunlight. Several target compounds and reactor platforms are considered and a comparison of state of the art biotechnological- and heterogeneous catalysis is performed. Target molecules include 4-Hydroxyprolin, methane, methanol, oxalic and tartaric acid.
 Diese Maßnahme wird mitfinanziert mit Steuermitteln auf Grundlage des von den Abgeordneten des Sächsischen Landtags beschlossenen Haushalts.
Diese Maßnahme wird mitfinanziert mit Steuermitteln auf Grundlage des von den Abgeordneten des Sächsischen Landtags beschlossenen Haushalts.
(This project is co-financed by means of taxation based on the budget adopted by the representatives of the Landtag of Saxony.)
How do sponges and bacteria together maintain productivity on coral reefs?
Integrating invertebrate biology, microbiology, genomics and metabolomics, this project aims to listen in on conversations between a Great Barrier Reef sponge and its bacterial symbionts. Coral reefs thrive in nutrient-poor tropical seas by relying on efficient retention and recycling of essential elements, and marine sponges are proving critically important in this role. They achieve this by cooperating with metabolically diverse bacterial symbionts via mechanisms that are largely unknown. Using the first and most advanced genome-enabled sponge in the world, this project seeks to reveal genomic and metabolic details of the partnership, with potential to inform environmental restoration, pharmaceuticals and biotechnology.
 The project is a collaboration with the Degnan labs at the University of Queensland (Brisbane, Australia) and funded through the Australian Research Council (DP170102353).
The project is a collaboration with the Degnan labs at the University of Queensland (Brisbane, Australia) and funded through the Australian Research Council (DP170102353).
The work of Jonas Wick and Claudius Lenz is dedicated to develop, maintain and utilize the large metabolite analysis resources within MIBITECH, the MIKAT analytics platform. Five HPLC and five GC devices are used as workhorses for standard quantification tasks in bioreactor systems.
On top our analytic research focuses mainly on the development of rugged MS-coupled analysis methods, that can cover a broad range of the microbial metabolome. While following a three-device approach (LC-HRMS, IC-HRMS and GC-MS) and consecutively optimizing sampling, data acquisition and analysis strategies, we can handle explorative and metabolomics tasks. Data thus generated is integrated into in-silico modelling to enhance research questions within fluxomics.
We also focus on fast reacting pools of redox-cofactors and energy metabolites, which are a major challenge when it comes to analysis, but are at the same time of tremendous importance for understanding the metabolic states within energy harvesting biotech setups.
 As a jointly appointed full professor at the Martin-Luther-University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU) and UFZ, Prof. Krömer (
Homepage
) is coordinating and teaching in two modules of the International Master for Pharmaceutical and Industrial Biotechnology at the Martin-Luther-University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU) in Halle (Saale).
As a jointly appointed full professor at the Martin-Luther-University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU) and UFZ, Prof. Krömer (
Homepage
) is coordinating and teaching in two modules of the International Master for Pharmaceutical and Industrial Biotechnology at the Martin-Luther-University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU) in Halle (Saale).
In winter semester, Module D 'Introduction to Bioprocess Technology' introduces key components of the bioprocess from enzymes, cellular catalysts, to bioreactors and reactor control. Dr. Bin Lai ( Homepage ) is serving as a co-lecturer here. During summer semester Module E 'Optimization of Bioprocesses' explores computational tools to describe and optimize the cell, the reactor, or the fermentation plant as a functional unit. During a practical at MLU, enzyme production and bioreactor operation is then practised in the wet-lab.
LC-MS/MS based proteomics analysis of Synechocystis sp. PCC6803 phenotype in biophotovoltaics
Understanding how Synechocystis behaviours exposing to anodic electron sink plays a central role in quantitative biophotovoltaics research and subsequent rational system engineering. The project aims to apply the lab-established LC-MS/MS methods to quantitatively address the proteome changes steered by the electrode. Two objectives will be focused on in this project, with each of them corresponding to an individual master thesis:
- Global proteome analysis focusing on cellular metabolism in response to different working conditions (e.g. light, working electrode potential, etc);
- Membrane proteome analysis with the target to identify key redox proteins involved in extracellular electron transfer or transporters responsible for mediator transportation.
CRISPR-based interrupting system (CRISPRi) for Synechocystis sp. PCC6803
This project is aiming to develop the CRISPRi system to targeted interrupt specific protein(s) of Synechocystis to identity its (their) functions involved in the performance of the microorganism in a biophotovoltaics system. The work will be based on a well-established system developed in KTH Sweden (Yao, L., et al. (2016). ACS Synthetic Biology 5(3): 207-212; Yao, L., et al. (2020). Nature Communications 11(1): 1666) and localize it into our lab. Essential strains and plasmids were kindly provided by Prof. Hudson. As a proof-of-concept study, the initial target will be to create a Synechocystis mutant with inducible inhibition of the photosystem II (PSII) protein complex. Different subunits of PSII should be tested and the time-course PSII activity (based on O2 evolution rate and PAM measurement) should be traced after induction.
Gas composition analysis using membrane-inlet mass spectrometry
This project aims for developing a quantitative protocol to trace the gas composition of the medium in BPV reactor. A membrane-inlet mass spectrometry will be used, and oxygen and CO2 are of particular interest in this project. Oxygen evolution rate and CO2 assimilation rate are the key parameters to be determined. The research question involved in this project is how the photosynthetic and carbon assimilation activities of Synechocystis sp PCC6803 are impacted by the anodic electron sink in BPV system.
Quantitative physiology of Synechocystis sp PCC6803 in response to light availability
Synechocystis is an important model organism for Cyanobacteria, which are considered as phototrophic platform organisms in biotechnology. This thesis aims at quantifying intracellular metabolite concentrations in response to light. These metabolites are the building blocks for biotechnological processes based on CO2. It will involve cultivation of microbes, sampling and mass spectrometry. Knowledge in microbial metabolism and a strong interest in quantitative work are desired.
Fluxomics of Cyanobacteria using 13C tracers
This project aims to determine uptake kinetics of isotopic tracers into the metabolism of Synechocystis sp. PCC6803. It will involve cultivation of microbes, sampling and mass spectrometry. A fundamental interest in microbiology and analytics is desired.
Photolysis of water in a bioelectrochemical system as a path to hydrogenporoduction
Hydrogen is considered a key energy carrier of the future. Splitting water into oxygen and hydrogen is a great way to generate H2. In this project we explore the capability of Cyanobacteria to catalyse this process and use an electrochemical system to separate H2. Being a fundamental research project, creativity and interest in electrochemical technology as well as microbiology are paramount.
