Microplastics, Nanoplastics, Elements
Our team focuses its research on three research fields:
- Nanoplastics
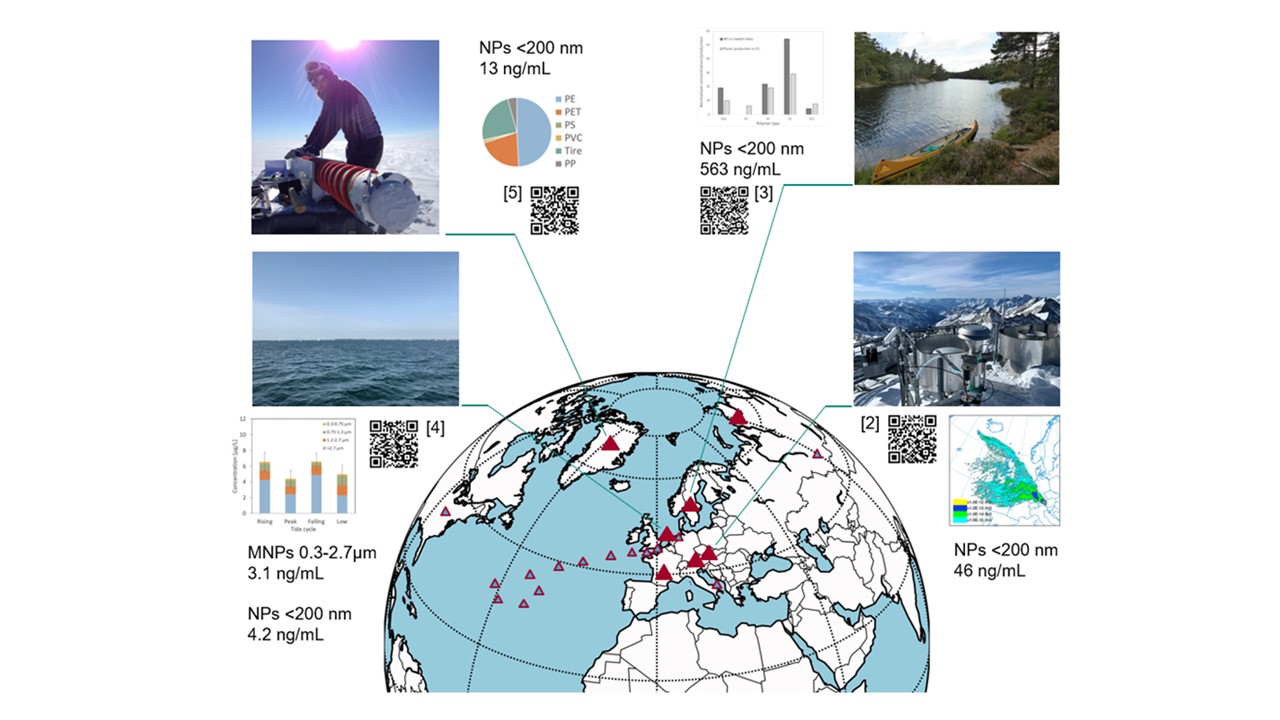
Our research focuses on assessing nanoplastic and microplastic pollution in different environmental compartments and biological samples. Using a novel experimental approach, we sensitively quantify nanoplastics using Thermal Desorption – Proton Transfer Reaction – Mass Spectrometry (TD-PTR-MS) [1]. We successfully measured nanoplastics in the Alps [2], rural surface water in Sweden and Siberia [3], the Dutch Wadden Sea [4], Greenland ice core and Antarctica sea ice [5] and European urban air [6]. - Microplastics
We use standard techniques to assess environmental and human-relevant microplastic pollution, such as FTIR and Raman spectroscopy. In our projects, we use innovative experimental approach that will first generate human exposure estimates after identification, measurement, and characterization of MNPLs present in the environmental air, water and food sources, as well as in human biological samples of population groups with potential high MNPLs exposure levels (biomonitoring study) by means of adapting the existing analytical methodology proven useful for fibres and nanomaterials. - Elemental and inorganic analysis
Our laboratory is equipped with high-end instrumentation and numerous experimental possibilities for particle characterization and quantification. We analyze particle size, particle composition and particle surface properties of inorganic and organic particles. In particular our lab is equipped with
Elemental analysis: ICP-MS (Thermo ICapQ, Element), ICP-OES (Spectro ARCOS)
Particle size fractionation: asymmetric flow-FFF (Wyatt Eclipse 3), rotating coiled column (RCC),
Particle sizing: dynamic light scattering (Nanostar, Wyatt), laser obscuration time analysis (Eyetech).
Elemental analysis in solid samples: laser ablation ICP-MS (G2 Analyte, Teledyne Cetac coupled to SpectroMS, Spectro at the ProVis facility
Polymer analysis: µFTIR imaging (Cary 620 FTIR Microscope, Cary 670 spectrometer, Agilent)
Further we have access to the instrumentation of the ProVis facility and Department of Analytical Chemistry including Raman spectroscopy and MALDI-MS
Scientists:
Dusan Materic
Guyu Peng
PhD students:
Orasai Faikhaw
Milena Latz
Steffen Weyrauch
Technicians:
Jennifer Heinle
Daniel Kolb
Karsten Marien
Madlen Zieseniß
Alumni / former colleagues
Hans-Joachim Stärk
Timothy Holbrook
Wen Qin
Robby Rynek
Ferdinand Krause
Josefine Karte
Jürgen Steffen
Ines Volkmann
Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme (EU): “PLASTICHEAL” 2023-2025 (https://www.plasticheal.eu/en)
NWO XS (Dutch Research Council): “Nanoplastics: hormone-mimicking and inflammatory responses?” 2019-2022
NWO XS (Dutch Research Council): “Size distribution of nanoplastics in indoor, urban and rural air” 2021-2023
INTERACT (EU): “Atmosphere-Snow Exchange of the Organic Matter”; 2018-2020
INTERACT (EU): “Nanoplastics In Remote Air: types, concentrations and size distribution” 2020-2022
NWO XS (Dutch Research Council): ”Mass spectrometry on steroids: identifying and quantifying nanoplastics in the ocean at trace levels (MASSIQ)” 2019-2020
NWO XS (Dutch Research Council): “Plastic in the air?” 2019-2020
NIOZ-UU (Dutch Research Council): “Nanoplastics in the Ocean” 2021-2025
CATALIST FUND (New Zeeland): Development of a standardised analytical method for measuring airborne microplastics 2021-2024
Selected Publications:
[1] D. Materić, A. Kasper-Giebl, D. Kau, M. Anten, M. Greilinger, E. Ludewig, E. van Sebille, T. Röckmann, R. Holzinger, Micro- and Nanoplastics in Alpine Snow: A New Method for Chemical Identification and (Semi)Quantification in the Nanogram Range, Environ. Sci. Technol. 54 (2020) 2353–2359. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.9b07540.
[2] D. Materić, E. Ludewig, D. Brunner, T. Röckmann, R. Holzinger, Nanoplastics transport to the remote, high-altitude Alps, Environ. Pollut. (2021) 117697. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117697.
[3] D. Materić, M. Peacock, J. Dean, M. Futter, T. Maximov, F. Moldan, T. Röckmann, R. Holzinger, Presence of nanoplastics in rural and remote surface waters, Environ. Res. Lett. 17 (2022) 054036. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/ac68f7.
[4] D. Materić, R. Holzinger, H. Niemann, Nanoplastics and ultrafine microplastic in the Dutch Wadden Sea – The hidden plastics debris?, Sci. Total Environ. 846 (2022) 157371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.157371.
[5] D. Materić, H.A. Kjær, P. Vallelonga, J.-L. Tison, T. Röckmann, R. Holzinger, Nanoplastics measurements in Northern and Southern polar ice, Environ. Res. 208 (2022) 112741. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2022.112741.
[6] B. Kirchsteiger, D. Materić, F. Happenhofer, R. Holzinger, A. Kasper-Giebl, Fine micro- and nanoplastics particles (PM2.5) in urban air and their relation to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, Atmos. Environ. 301 (2023) 119670. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2023.119670.
[7] D. Materić, E. Ludewig, K. Xu, T. Röckmann, R. Holzinger, Brief communication: Analysis of organic matter in surface snow by PTR-MS – implications for dry deposition dynamics in the Alps, The Cryosphere. 13 (2019) 297–307. https://doi.org/10.5194/tc-13-297-2019.
[8] D. Materić, M. Peacock, M. Kent, S. Cook, V. Gauci, T. Röckmann, R. Holzinger, Characterisation of the semi-volatile component of Dissolved Organic Matter by Thermal Desorption – Proton Transfer Reaction – Mass Spectrometry, Sci. Rep. 7 (2017) 15936. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-16256-x.
[9] S. Allen, D. Materić, D. Allen, A. MacDonald, R. Holzinger, G.L. Roux, V.R. Phoenix, An early comparison of nano to microplastic mass in a remote catchment’s atmospheric deposition, J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 7 (2022) 100104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hazadv.2022.100104.
[10] R. Holzinger, W.J.F. Acton, W.J. Bloss, M. Breitenlechner, L.R. Crilley, S. Dusanter, M. Gonin, V. Gros, F.N. Keutsch, A. Kiendler-Scharr, L.J. Kramer, J.E. Krechmer, B. Languille, N. Locoge, F. Lopez-Hilfiker, D. Materić, S. Moreno, E. Nemitz, L.L.J. Quéléver, R. Sarda Esteve, S. Sauvage, S. Schallhart, R. Sommariva, R. Tillmann, S. Wedel, D.R. Worton, K. Xu, A. Zaytsev, Validity and limitations of simple reaction kinetics to calculate concentrations of organic compounds from ion counts in PTR-MS, Atmospheric Meas. Tech. 12 (2019) 6193–6208. https://doi.org/10.5194/amt-12-6193-2019.
[11] D. Allen, S. Allen, S. Abbasi, A. Baker, M. Bergmann, J. Brahney, T. Butler, R.A. Duce, S. Eckhardt, N. Evangeliou, T. Jickells, M. Kanakidou, P. Kershaw, P. Laj, J. Levermore, D. Li, P. Liss, K. Liu, N. Mahowald, P. Masque, D. Materić, A.G. Mayes, P. McGinnity, I. Osvath, K.A. Prather, J.M. Prospero, L.E. Revell, S.G. Sander, W.J. Shim, J. Slade, A. Stein, O. Tarasova, S. Wright, Microplastics and nanoplastics in the marine-atmosphere environment, Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 3 (2022) 393–405. https://doi.org/10.1038/s43017-022-00292-x.
[12] M. Peacock, D. Materić, D.N. Kothawala, R. Holzinger, M.N. Futter, Understanding Dissolved Organic Matter Reactivity and Composition in Lakes and Streams Using Proton-Transfer-Reaction Mass Spectrometry (PTR-MS), Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 5 (2018) 739–744. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.estlett.8b00529.
[13] Peng, G., Lin, Y., van Bavel, B., Li, D., Ni, J. and Song, Y. 2022. Aggregate exposure pathways for microplastics (mpAEP): An evidence-based framework to identify research and regulatory needs. Water Research 209, 117873.
[14] Peng, G., Xu, B. and Li, D. 2022. Gray Water from Ships: A Significant Sea-Based Source of Microplastics? Environmental Science & Technology 56(1), 4-7.
Selected Publications:
[1] D. Materić, A. Kasper-Giebl, D. Kau, M. Anten, M. Greilinger, E. Ludewig, E. van Sebille, T. Röckmann, R. Holzinger, Micro- and Nanoplastics in Alpine Snow: A New Method for Chemical Identification and (Semi)Quantification in the Nanogram Range, Environ. Sci. Technol. 54 (2020) 2353–2359. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.9b07540.
[2] D. Materić, E. Ludewig, D. Brunner, T. Röckmann, R. Holzinger, Nanoplastics transport to the remote, high-altitude Alps, Environ. Pollut. (2021) 117697. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117697.
[3] D. Materić, M. Peacock, J. Dean, M. Futter, T. Maximov, F. Moldan, T. Röckmann, R. Holzinger, Presence of nanoplastics in rural and remote surface waters, Environ. Res. Lett. 17 (2022) 054036. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/ac68f7.
[4] D. Materić, R. Holzinger, H. Niemann, Nanoplastics and ultrafine microplastic in the Dutch Wadden Sea – The hidden plastics debris?, Sci. Total Environ. 846 (2022) 157371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.157371.
[5] D. Materić, H.A. Kjær, P. Vallelonga, J.-L. Tison, T. Röckmann, R. Holzinger, Nanoplastics measurements in Northern and Southern polar ice, Environ. Res. 208 (2022) 112741. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2022.112741.
[6] B. Kirchsteiger, D. Materić, F. Happenhofer, R. Holzinger, A. Kasper-Giebl, Fine micro- and nanoplastics particles (PM2.5) in urban air and their relation to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, Atmos. Environ. 301 (2023) 119670. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2023.119670.
[7] D. Materić, E. Ludewig, K. Xu, T. Röckmann, R. Holzinger, Brief communication: Analysis of organic matter in surface snow by PTR-MS – implications for dry deposition dynamics in the Alps, The Cryosphere. 13 (2019) 297–307. https://doi.org/10.5194/tc-13-297-2019.
[8] D. Materić, M. Peacock, M. Kent, S. Cook, V. Gauci, T. Röckmann, R. Holzinger, Characterisation of the semi-volatile component of Dissolved Organic Matter by Thermal Desorption – Proton Transfer Reaction – Mass Spectrometry, Sci. Rep. 7 (2017) 15936. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-16256-x.
[9] S. Allen, D. Materić, D. Allen, A. MacDonald, R. Holzinger, G.L. Roux, V.R. Phoenix, An early comparison of nano to microplastic mass in a remote catchment’s atmospheric deposition, J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 7 (2022) 100104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hazadv.2022.100104.
[10] R. Holzinger, W.J.F. Acton, W.J. Bloss, M. Breitenlechner, L.R. Crilley, S. Dusanter, M. Gonin, V. Gros, F.N. Keutsch, A. Kiendler-Scharr, L.J. Kramer, J.E. Krechmer, B. Languille, N. Locoge, F. Lopez-Hilfiker, D. Materić, S. Moreno, E. Nemitz, L.L.J. Quéléver, R. Sarda Esteve, S. Sauvage, S. Schallhart, R. Sommariva, R. Tillmann, S. Wedel, D.R. Worton, K. Xu, A. Zaytsev, Validity and limitations of simple reaction kinetics to calculate concentrations of organic compounds from ion counts in PTR-MS, Atmospheric Meas. Tech. 12 (2019) 6193–6208. https://doi.org/10.5194/amt-12-6193-2019.
[11] D. Allen, S. Allen, S. Abbasi, A. Baker, M. Bergmann, J. Brahney, T. Butler, R.A. Duce, S. Eckhardt, N. Evangeliou, T. Jickells, M. Kanakidou, P. Kershaw, P. Laj, J. Levermore, D. Li, P. Liss, K. Liu, N. Mahowald, P. Masque, D. Materić, A.G. Mayes, P. McGinnity, I. Osvath, K.A. Prather, J.M. Prospero, L.E. Revell, S.G. Sander, W.J. Shim, J. Slade, A. Stein, O. Tarasova, S. Wright, Microplastics and nanoplastics in the marine-atmosphere environment, Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 3 (2022) 393–405. https://doi.org/10.1038/s43017-022-00292-x.
[12] M. Peacock, D. Materić, D.N. Kothawala, R. Holzinger, M.N. Futter, Understanding Dissolved Organic Matter Reactivity and Composition in Lakes and Streams Using Proton-Transfer-Reaction Mass Spectrometry (PTR-MS), Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 5 (2018) 739–744. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.estlett.8b00529.
[13] Peng, G., Lin, Y., van Bavel, B., Li, D., Ni, J. and Song, Y. 2022. Aggregate exposure pathways for microplastics (mpAEP): An evidence-based framework to identify research and regulatory needs. Water Research 209, 117873.
[14] Peng, G., Xu, B. and Li, D. 2022. Gray Water from Ships: A Significant Sea-Based Source of Microplastics? Environmental Science & Technology 56(1), 4-7.
