Effect-based Human Biomonitoring (EB-HBM)
The production and release of synthetic chemicals results in an exposure of humans and the environment to complex mixture of organic pollutants. Accordingly, chemicals are an essential part of the (human) exposome, which encompasses all non-genetic and external factors that may influence health. The sheer diversity of this chemical exposome poses a great challenge, as with current technology we cannot decipher all chemical features that pose a threat to (human) health at once.
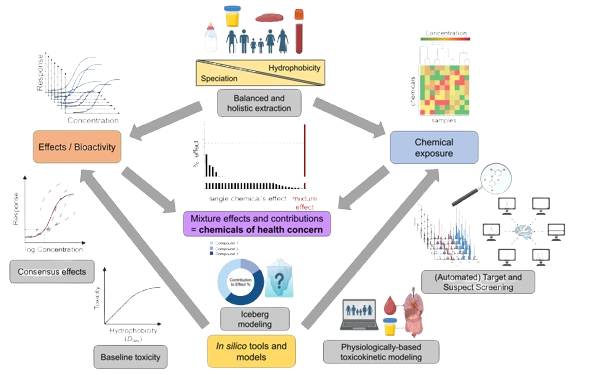
To address this challenge, we developed an effect-based human biomonitoring (EB-HBM) approach that allows to prioritize and identify bioactive chemicals and their mixtures. In this EB-HBM framework, we combine in silico tools and models with both exposure and effect data from human samples in a high-throughput and automated manner. In silico tools are used to prioritize chemical mixtures for inclusion in chemical analysis bioanalysis.
Initially, the chemical exposure is predicted from occurrence data via physiologically-based toxicokinetic models and mixture compositions in virtual populations, which is linked to curated bioactivity data to prioritize chemicals of concern in silico. We analyze samples from different human matrices (e.g., blood, breast milk, tissues and organs) and make use of holistic and balanced extraction techniques such as passive equilibrium sampling (PES) in combination with solid-phase extraction (SPE), to recover as complex and representative mixtures as possible. For the exposure assessment we use high-resolution mass spectrometry for a diverse set of analytes, and utilize automated suspect and target screening workflows to facilitate a high throughput. The same sample extracts are then employed to cell-based in vitro bioassays targeting relevant health endpoints (e.g., endocrine disruption, developmental neurotoxicity, immunotoxicity, metabolic disruption) to promote the direct link of exposure and effect of chemicals and their mixtures.
More information: Braun, G.; Herberth, G.; Krauss, M.; König, M.; Wojtysiak, N.; Zenclussen, A. C.; Escher, B. I., Neurotoxic mixture effects of chemicals extracted from blood of pregnant women. Science 2024
