Daniel Doktor, Dr.

Head of working group
Helmholtz Centre for Environmental Research - UFZ
Department Remote Sensing
Permoserstrasse 15, 04318 Leipzig - Germany
Tel.: +49 (0) 341 / 6025 1943
Daniel Doktor
Full member of German Centre for Integrative Biodiversity Research (iDiv)
Profile
- Within the context of analysing the impacts of climate and global change on vegetation, my research focus is on the land-use, land-use intensity, plant traits and ecosystem services.
- Acquistion and leading of third party funded projects (BMWI, BfN, BMEL, Helmholtz Association, EU)
- Collaboration in UFZ's program oriented research (POF) and strategic processes, e.g. establishment of the Centre for Remote Sensing (RSC4Earth) in cooperation with Leipzig University
My research focuses on the detection and evaluation of climate (extreme) effects and land-use / land-cover change on terrestrial vegetation. This concerns the following components:
1. Analysing optical-reflective time-series of satellite data to derive forest condition, plant traits (phenology, pigments, leaf area) and ecosystem services (biodiversity, productivity). This is done by inverse parameterisation of radiative transfer models, classical empirical approaches as well as data science methods.
2. Acquisition of remotely sensed hyperspectral (airborne and field) data accompanied by respective trait measurements and in-situ vegetation records
3. Derivation of land-use (crop types, tree species), land-use intensity (mowing events, grazing intensity, fertilisation) and habitats from optical-reflective time-series of satellite data using data science methods
4. Establish / evaluate links between land-use intensity / biodiversity and plant traits / vegetation condition
Education
- 1994 Abitur, Martin-Luther-Schule, Marburg
- 1996-2002 Studies of Geography at the Westfälische Wilhelms Universität Münster, Diplom
- 1998-1999 Studies of Geography at the Universität Rouen, France
- 2003-2007 PhD at Imperial College, London
Non-academic
- 1994-1995 Civil Service, Universitätsklinikum Marburg
Academic posts
- since 2008 Postdoc at the Helmholtz Centre for Environmental Research - UFZ, Leader of the group 'Land-Cover & Dynamics' (LACY)'
- 2007-2008 Research Associate, Imperial College London, Falklands Group
- 2003-2007 PhD, Imperial College (London, U.K.), Department of Biology: Using satellite imagery and ground observations to quantify the effect of intra-annually changing temperature patterns on spring time phenology. Project: 'Time Geographical approaches to Emergence and Sustainable Societies' (TiGrESS)
- 2002-2003 Research Associate, Potsdam Institute of Climate Impact Research (PIK); Projects: 'Sensitivity and Adaptation of Forests under Global Change' (SAFE) and 'Climate Change Adaptility of Wine' (CLAWINE)
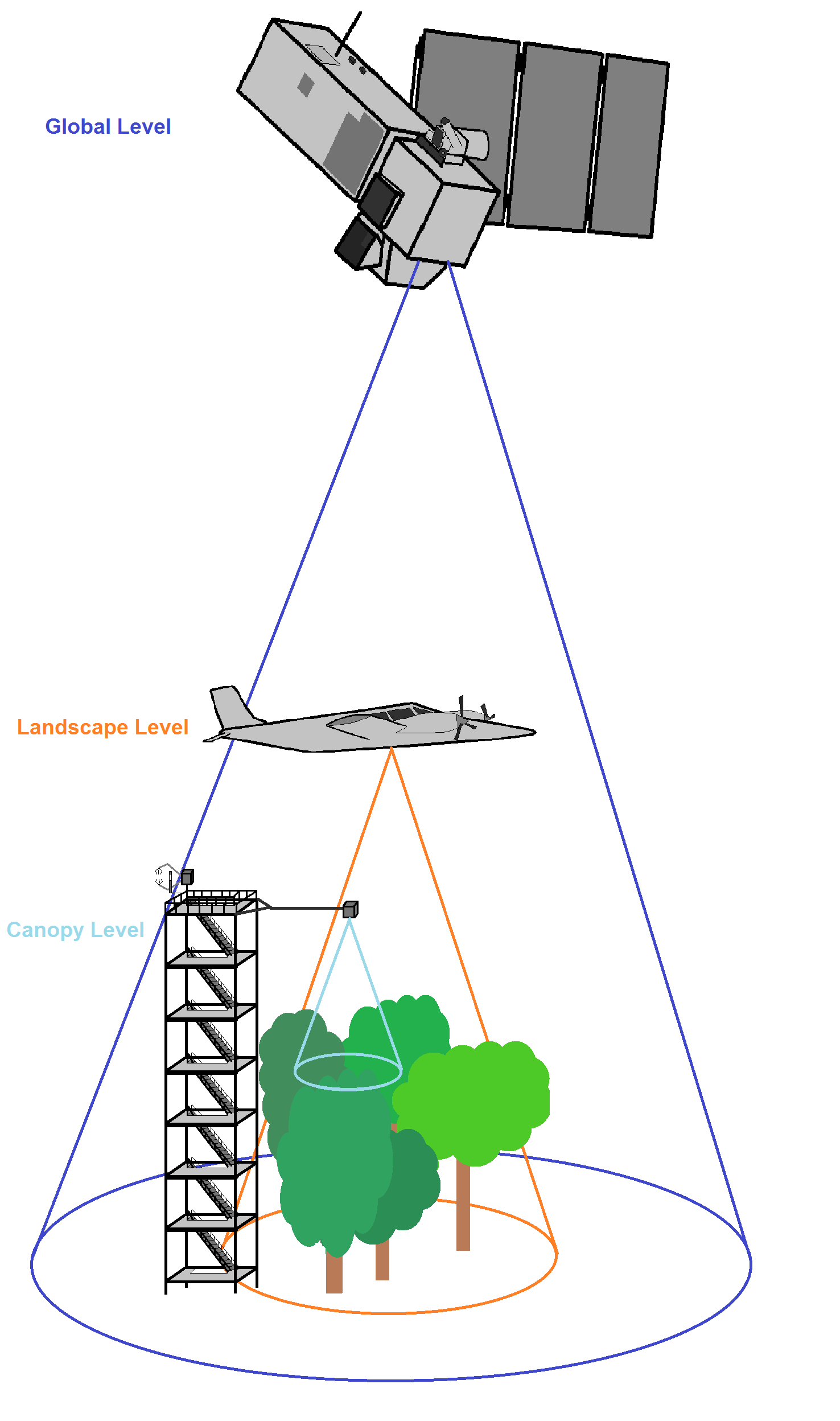
New developments strengthen the link between modelling and remote sensing and sensor fusion, e.g. Helmholtz Alliance ‘Earth System Dynamics’ (http://hgf-eda.de/). Furthermore, large-scale validation sites for remote sensing products including spectral sensor networks are being establishment (Sentinel Missions, ACROSS, GCEF). Data are gathered at different spatial scales covering also micro-meteorological, biological and hydrological aspects (EnMAP project) to facilitate up-scaling (s. Figures below).

Extracting & simulating phenological metrics
The focus within vegetation phenology is on analysing the response of spring time phenology to climate change using ground and satellite observations. We also assessed the influence of heterogeneous landscapes on computed green-up dates and analysed trends of computed green-up dates on a European scale. A variety of methods to extract phenological metrics has been implemented in R package ’phenex’ to be of public use.
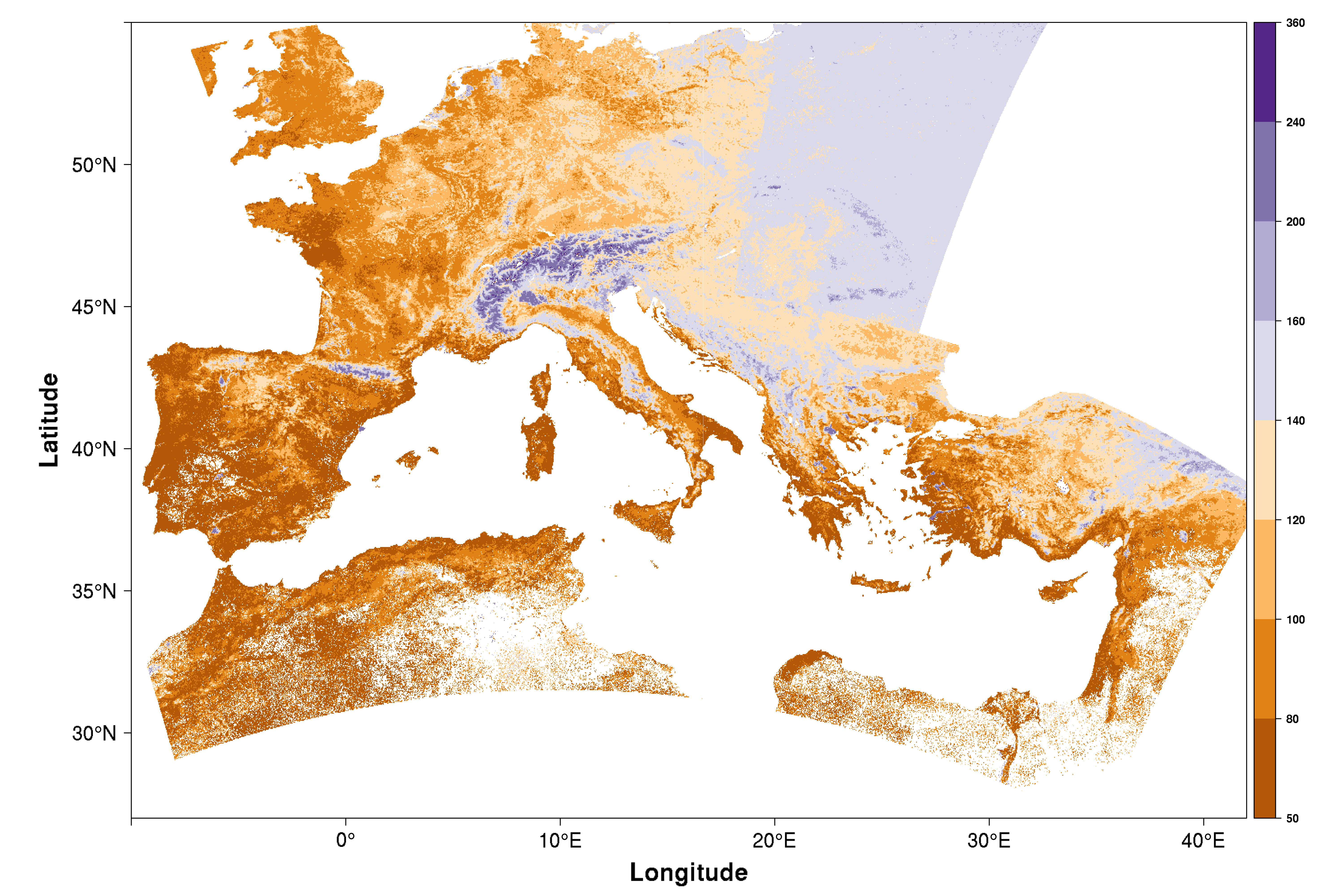
Physical-based phenological modelling
Coupling remote sensing with ecosystem modelling faclitates a better understanding of how bio-physical processes on the earth's surface translate into an electromagnetic signal received by e.g. a satellite sensor. Here, we employ a model driven by temperature and day length (PIM) to simulate phenological growth stages of tree species.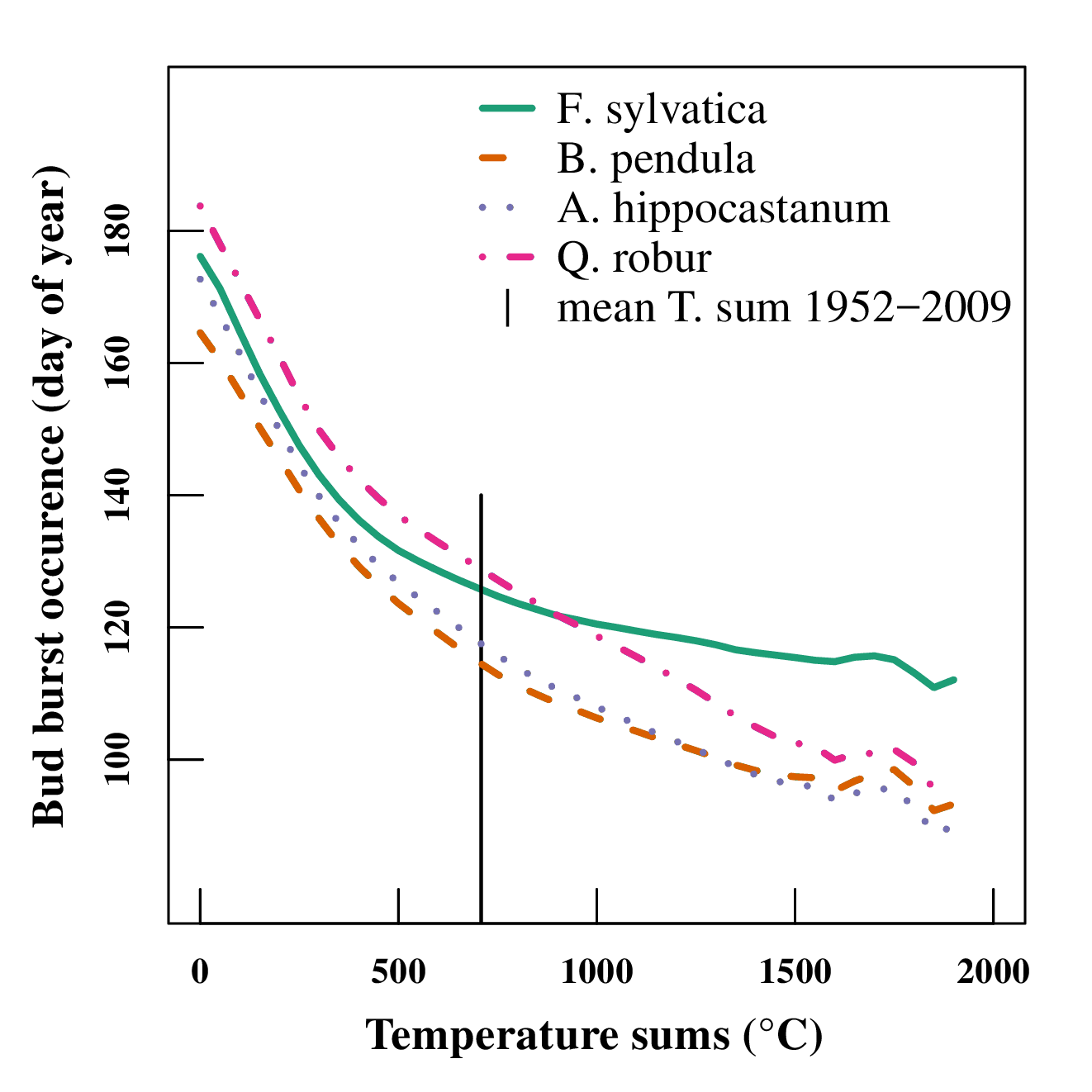
In: Lange, M., Schaber, J., Marx, A., Jäckel, G., Badeck, F.W., Seppelt, R., Doktor, D. (2016). Simulation of forest tree species' phenological phases for different climate scenarios: chilling requirements and photo-period may limit bud burst advancement". International Journal of Biometeorology. DOI 10.1007/s00484-016-1161-8
Extraction of biopyhsical vegetation variables
The inversion of radiative transfer models is at the heart of determining e.g. Chlorophyll or water content of vegetation. The figure below shows simulated reflection profiles of vegetation based on 4 parameters sets with increasing complexity (+ noise) using PROSAIL.
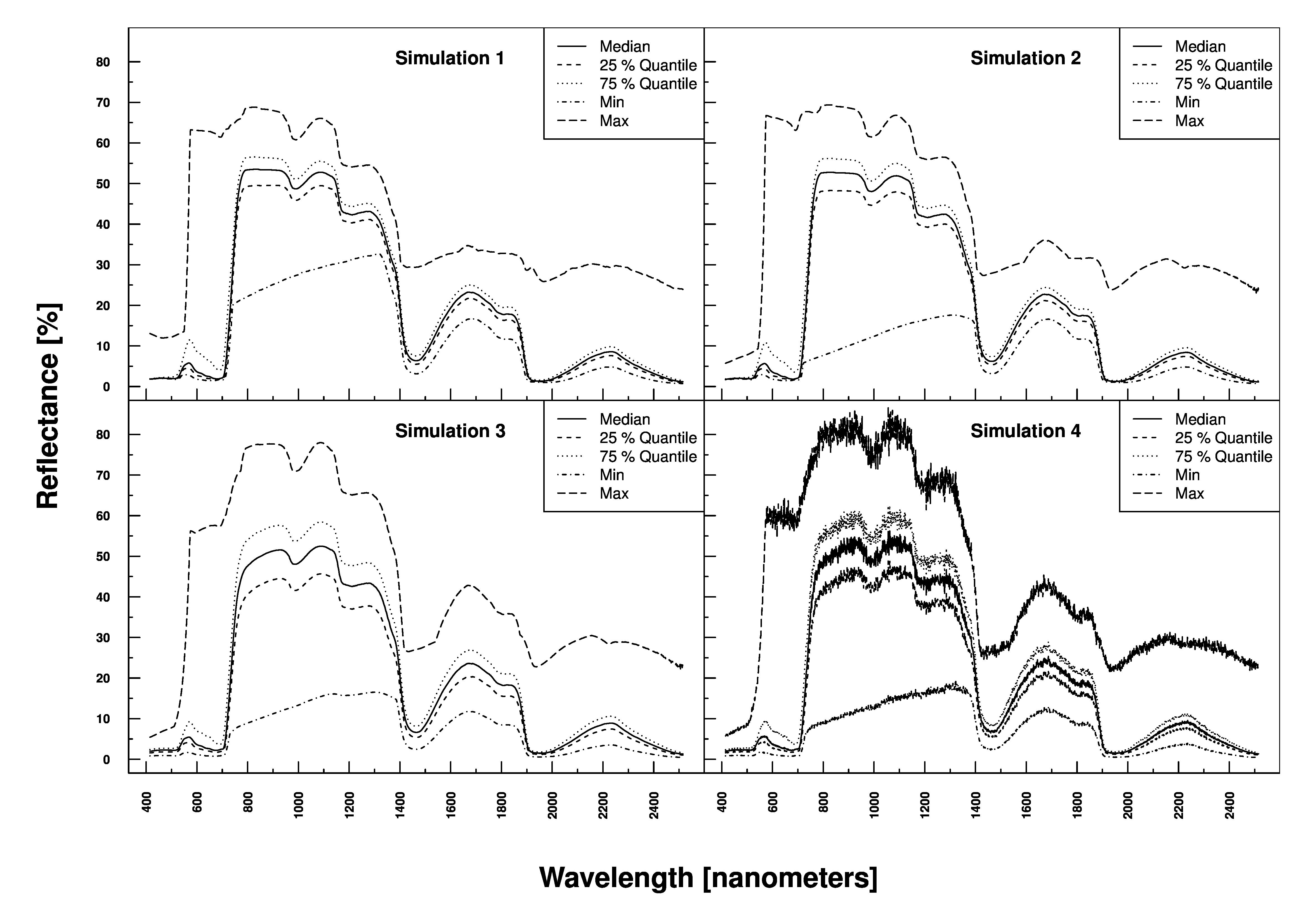
Radiative Transfer Modelling
The working group is also simulating at-sensor radiances by combining two models: the vegetation radiative transfer model SLC and the atmosphere radiative transfer model MODTRAN. This allows to work with signals received directly at the sensor, which makes it easier to identify vegetation parameters. Furthermore, this procedure reduces the number of variables for inversion and the overall computational effort required.
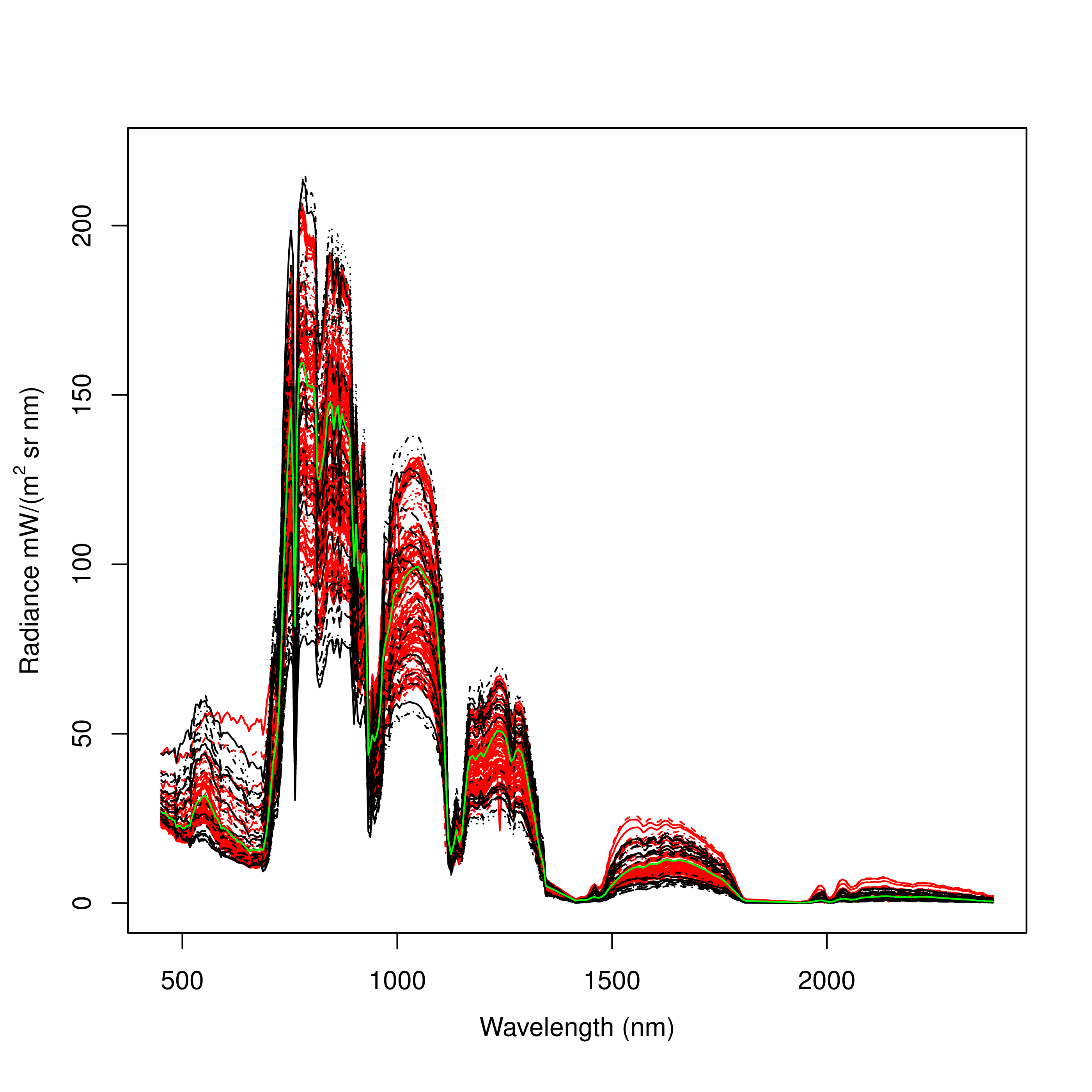
Measured at-sensor radiances (AISA dual) and simulated radiances of vegetation (wheat). red=at-sensor radiances, green=mean at-sensor radiances, black=simulated radiances. Preidl, S. A new framework for radiative transfer model inversion (in prep.)
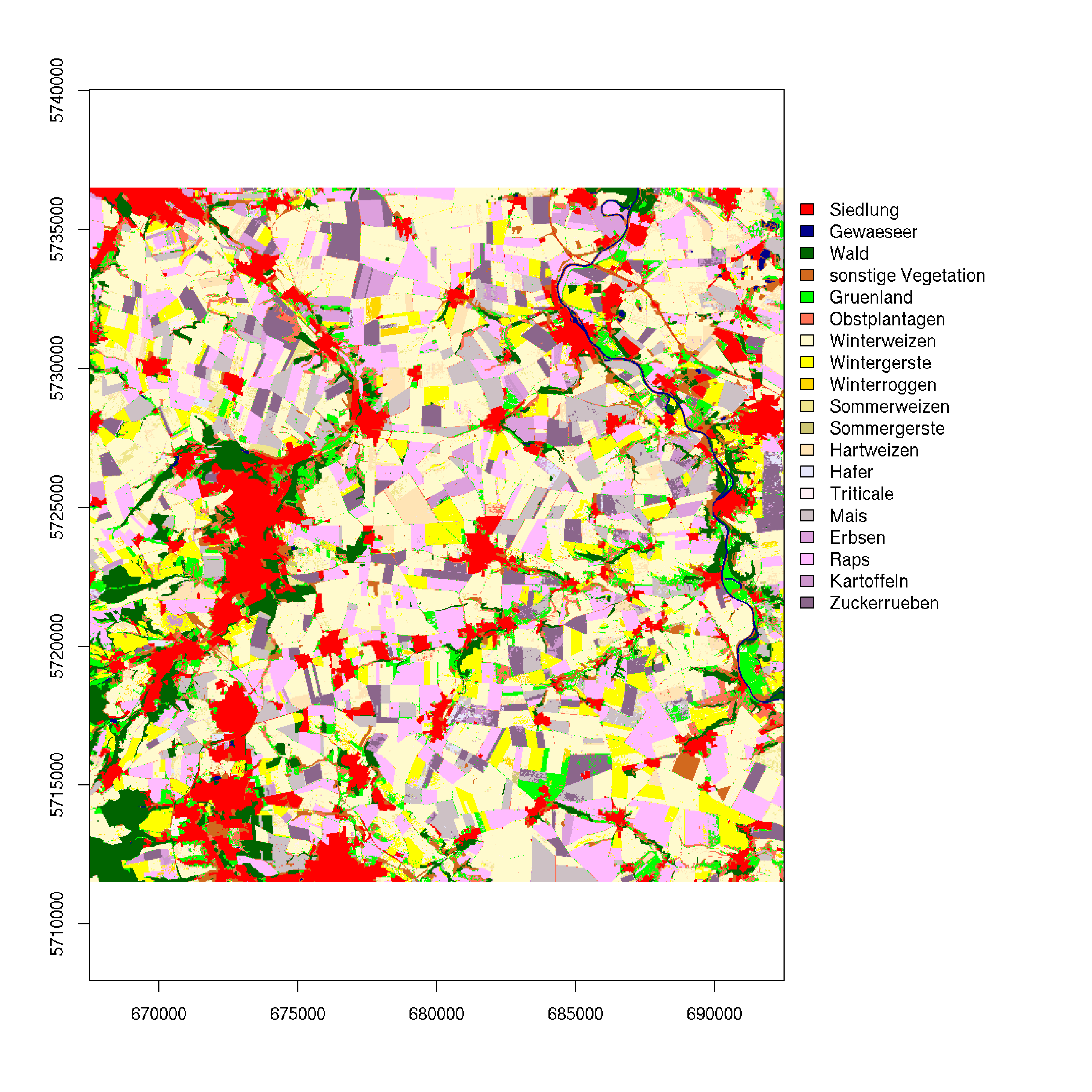
Land-use classification, habitat & biodiversity mapping
This is actually an old (remote sensing) topic which has seen a renaissance in the light of new satellite missions. This allows for example to discriminate tree species or to map crop types at field level (as shown below).
The link between pollination types at the community level and optical traits allows us to map spatial patterns of pollination types with remotely sensed hyperspectral data.
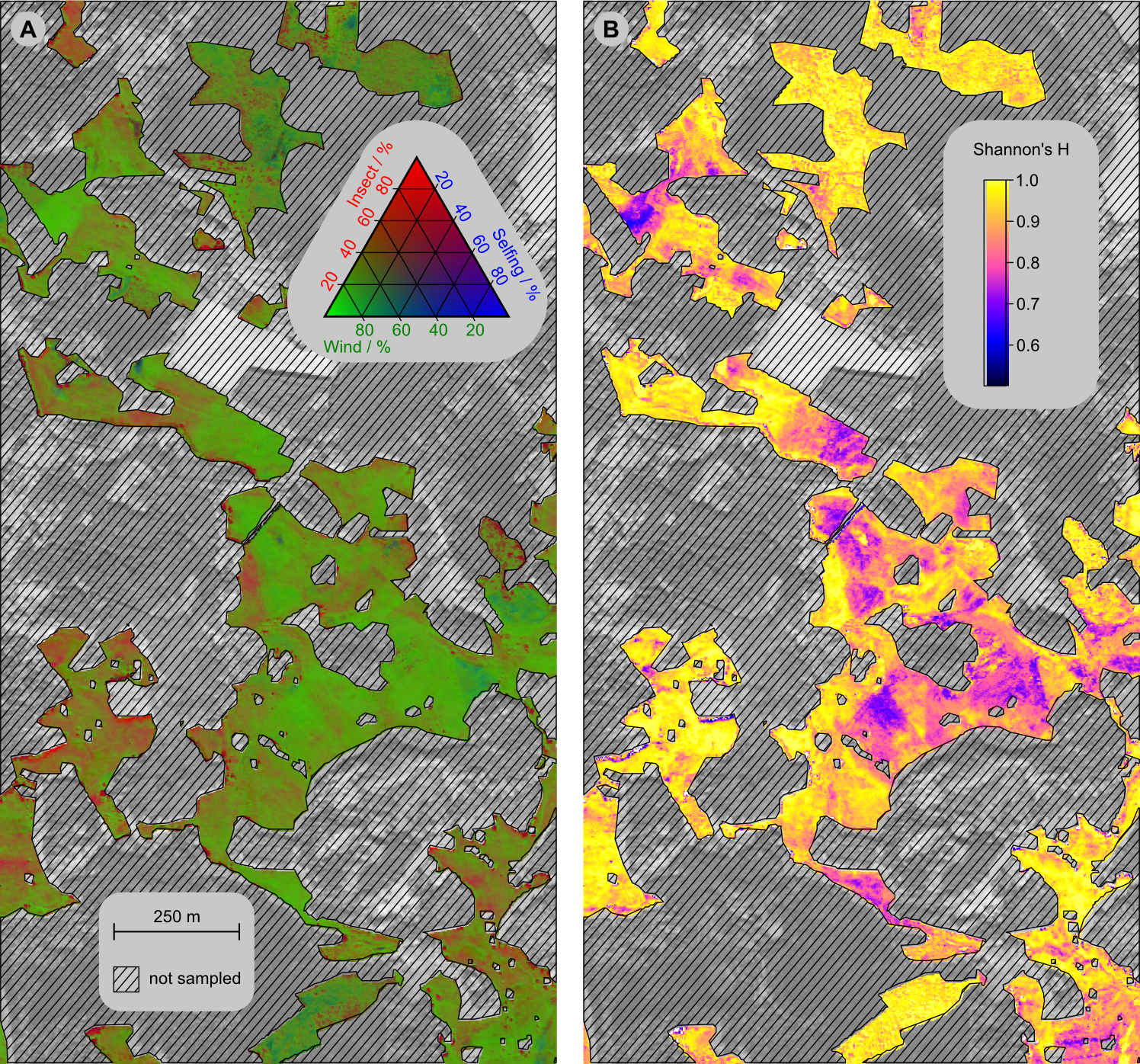
Distribution of the pollination types across the study site (a) and Shannon’s entropy H of the three pollination types (b) as mapped from airborne imaging spectroscopy data. Forested and agricultural areas were not covered by the sampling and thus masked. Feilhauer, H., Doktor, D., Schmidtlein, S., Skidmore, A. (2016). Mapping pollination types with remote sensing, Journal of Vegetation Science 27. pp. 999-1011
- Radiative transfer modelling (PROSAIL, SLC, DART)
- Data Sciene methods such as machine learning (PCA, randomForest, PLSR, SVR, Gaussian processes), geostatistics
- Radiometric, geometric and atmospheric correction of hyperspectral data
- High performance cluster computation
Ongoing
- Helmholtz Association: "Impacts of hydroclimatic extremes on long- term forest condition anomalies" (PI) in PhD cohort "Societal and Environmental impacts of complex ExtremeS in a chAnging World" (2025-2029)
- Federal Ministry for Food and Agriculture (BMEL): "Waldresilienz" (2024-2025)
- "KI-basierte Integration von Fernerkundungs- und Citizen-Science- Daten zur Ableitung der Biodiversität in Wäldern" (iForest). Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF).
(2023-2024) - Flexpool funding iDiv: "Towards robust detection of plant diversity & management in grasslands’ spectral signal", PI (2022-2024)
- UFZ PhD colleg MoDEV, project "Assessment of species and trait diversity in temperate vegetation from optical remote sensing data". With Leipzig University, Prof. Feilhauer (2021-2024)
- Helmholtz Knowledge Transfer Project "Waldzustandsmonitor" (2021-2024)
Finished
- EU 'Ecopotential' ('Horizon 2020'). 'Derivation of bio-physical variables from remotely sensed imagery' (2015-2018)
- BMWi program ‚Vorbereitung der wissenschaftlichen und kommerziellen Nutzung der Sentinel-Missionen und nationalen Missionen‘: ‚PhenoS - Phänologische Strukturierung von zeitlich hochauflösenden Sentinel 2- Datensätzen zur Optimierung von Landnutzungsklassifikationen‘ (2013- 2017)
- Helmholtz-Alliance ‘Remote Sensing and Earth System Dynamics’ (Biosphere): 'Fusion of radar (L-band) and hyperspectral data to derive biomass, leaf area index and vegetation disturbance' (2012-2017)
- BfN assignement on ‚Characterisation of forest types using remotely sensed imagery‘ (2016)
- BMWi program ‚Vorbereitung der wissenschaftlichen und kommerziellen Nutzung der Sentinel-Missionen und nationalen Missionen‘: ‘Validierung von Sentinel-Produkten auf Basis kontinuierlicher spektraler und Eddy- Flux-Messungen’ (2012-2015)
- BMWi program ‚Development of methods and algorithms for data analysis in preparation of the EnMAP mission': ‘Methoden zur Ableitung des funktionellen Zusammenhanges ökosystemarer Prozesse in hyperspektralen Daten unterschiedlicher räumlicher Auflösung’ (2010- 2013)
- Project within ‚Ecosystem Services under Changing Land-use and Climate‘ (ESCALATE, http://www.ufz.de/escalate/): Ecosystem services assessment in a Central European floodplain forest: an ecosystem approach using reflective and thermal remote sensing data (2013-2016)
Integrated projects (IP, UFZ funded):
Within the topic 'From local scale processes to regional predictions' (T53) =>
- "Estimation of terrestrial gross primary production (GPP) from remote sensing data“ (2013-2017)
- "Modelling and measuring fluorescence of a deciduous forest" (2016-2019)
Index:
- 2025 (6)
- 2024 (6)
- 2022 (3)
- 2021 (1)
- 2020 (3)
- 2018 (1)
- 2017 (5)
- 2016 (6)
- 2015 (2)
- 2014 (3)
- 2013 (5)
- 2012 (1)
- 2011 (1)
- 2009 (1)
You could use our publication index for further requests.
2025 (6)
- Iakunin, M., Goss, R., Doktor, D. (2025):
Grassland management and phenology affect trait retrieval accuracy from remote sensing observations - field campaign dataset
Zenodo 10.5281/zenodo.14777369 - Iakunin, M., Taubert, F., Goss, R., Sasso, S., Feilhauer, H., Doktor, D. (2025):
Grassland management and phenology affect trait retrieval accuracy from remote sensing observations
Ecol. Inform. 87 , art. 103068 10.1016/j.ecoinf.2025.103068 - Ludwig, A., Feilhauer, H., Doktor, D. (2025):
Exploring Sentinel-2-based spectral variability for enhancing grassland diversity assessments across Germany
Appl. Veg. Sci. 28 (3), e70030 10.1111/avsc.70030 - Rahmsdorf, E., Doktor, D., Feilhauer, H., Brede, B., Dienstbach, L., Eisenhauer, N., Hildebrandt, A., Rüger, N., Lange, M. (2025):
Drivers of remotely sensed tree height heterogeneity across spatial scales: Tree species diversity effects depend on local conditions and forest type
Ecol. Indic. 179 , art. 114245 10.1016/j.ecolind.2025.114245 - Reichmuth, A., Kühn, I., Schmidt, A., Doktor, D. (2025):
Forested Natura 2000 sites under climate change: effects of tree species distribution shifts
Web Ecol. 25 (1), 59 - 89 10.5194/we-25-59-2025 - Reichmuth, A., Rakovec, O., Boeing, F., Müller, S., Samaniego, L., Marx, A., Komischke, H., Schmidt, A., Doktor, D. (2025):
BioVars - A bioclimatic dataset for Europe based on a large regional climate ensemble for periods in 1971–2098
Sci. Data 12 , art. 217 10.1038/s41597-025-04507-w
2024 (6)
- Lange, M., Preidl, S., Reichmuth, A., Heurich, M., Doktor, D. (2024):
Forest condition anomaly index values covering Germany for 2016-2023 (7.5.0) [Data set]
Zenodo 10.5281/zenodo.13123397 - Lange, M., Preidl, S., Reichmuth, A., Heurich, M., Doktor, D. (2024):
A continuous tree species-specific reflectance anomaly index reveals declining forest condition between 2016 and 2022 in Germany
Remote Sens. Environ. 312 , art. 114323 10.1016/j.rse.2024.114323 - Ludwig, A., Doktor, D., Feilhauer, H. (2024):
Is spectral pixel-to-pixel variation a reliable indicator of grassland biodiversity? A systematic assessment of the spectral variation hypothesis using spatial simulation experiments
Remote Sens. Environ. 302 , art. 113988 10.1016/j.rse.2023.113988 - Mahecha, M.D., Bastos, A., Bohn, F.J., Eisenhauer, N., Feilhauer, H., Hickler, T., Kalesse-Los, H., Migliavacca, M., Otto, F.E.L., Peng, J., Sippel, S., Tegen, I., Weigelt, A., Wendisch, M., Wirth, C., Al-Halbouni, D., Deneke, H.M., Doktor, D., Dunker, S., Duveiller, G., Ehrlich, A., Foth, A., García-García, A., Guerra, C.A., Guimarães- Steinicke, C., Hartmann, H., Henning, S., Herrmann, H., Hu, P., Ji, C., Kattenborn, T., Kolleck, N., Kretschmer, M., Kühn, I., Luttkus, M.L., Maahn, M., Mönks, M., Mora, K., Pöhlker, M., Reichstein, M., Rüger, N., Sánchez-Parra, B., Schäfer, M., Stratmann, F., Tesche, M., Wehner, B., Wieneke, S., Winkler, A.J., Wolf, S., Zaehle, S., Zscheischler, J., Quaas, J. (2024):
Biodiversity and climate extremes: known interactions and research gaps
Earth Future 12 (6), e2023EF003963 10.1029/2023EF003963 - Meshkini, K., Bovolo, F., Doktor, D. (2024):
Attention-based 3D convolutional neural network for crop boundary detection in high-resolution satellite image time series
In: Bruzzone, L., Bovolo, F. (eds.)
Artificial Intelligence and Image and Signal Processing for Remote Sensing XXX 2024, Edinburgh, 16-18 September 2024
Proceedings / SPIE 13196
SPIE, Bellingham, WA, p. 131960E 10.1117/12.3035893 - Reichmuth, A., Rakovec, O., Boeing, F., Müller, S., Samaniego, L., Marx, A., Komischke, H., Doktor, D. (2024):
BioVars - bioclimatic datasets for Europe based on a large regional climate ensemble for periods between 1971 to 2098 (1.1.0) [Data set]
Zenodo 10.5281/zenodo.14624171
2022 (3)
- Hase, N., Doktor, D., Rebmann, C., Dechant, B., Mollenhauer, H., Cuntz, M. (2022):
Identifying the main drivers of the seasonal decline of near-infrared reflectance of a temperate deciduous forest
Agric. For. Meteorol. 313 , art. 108746 10.1016/j.agrformet.2021.108746 - Lange, M., Feilhauer, H., Kühn, I., Doktor, D. (2022):
Mapping land-use intensity of grasslands in Germany with machine learning and Sentinel-2 time series
Remote Sens. Environ. 277 , art. 112888 10.1016/j.rse.2022.112888 - Ludwig, A.D., Doktor, D., Goss, R., Sasso, S., Feilhauer, H. (2022):
The leaf is always greener on the other side of the lab: Optical in-situ indicators for leaf chlorophyll content need improvement for semi-natural grassland areas
Ecol. Indic. 143 , art. 109424 10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.109424
2021 (1)
- Feilhauer, H., Zlinszky, A., Kania, A., Foody, G.M., Doktor, D., Lausch, A., Schmidtlein, S. (2021):
Let your maps be fuzzy!—Class probabilities and floristic gradients as alternatives to crisp mapping for remote sensing of vegetation
Remote Sens. Ecol. Conserv. 7 (2), 292 - 305 10.1002/rse2.188
2020 (3)
- Ayalew, D.A., Deumlich, D., Šarapatka, B., Doktor, D. (2020):
Quantifying the sensitivity of NDVI-based C factor estimation and potential soil erosion prediction using spaceborne Earth observation data
Remote Sens. 12 (7), art. 1136 10.3390/rs12071136 - Kattge, J., Bönisch, G., Díaz, S., Lavorel, S., Beckmann, M., Dechant, B., Durka, W., Klotz, S., Roscher, C., Doktor, D., Prentice, I.C., et al. (2020):
TRY plant trait database – enhanced coverage and open access
Glob. Change Biol. 26 (1), 119 - 188 10.1111/gcb.14904 - Preidl, S., Lange, M., Doktor, D. (2020):
Introducing APiC for regionalised land cover mapping on the national scale using Sentinel-2A imagery
Remote Sens. Environ. 240 , art. 111673 10.1016/j.rse.2020.111673
2018 (1)
- Rocchini, D., Luque, S., Pettorelli, N., Bastin, L., Doktor, D., Faedi, N., Feilhauer, H., Féret, J.-B., Foody, G.M., Gavish, Y., Godinho, S., Kunin, W.E., Lausch, A., Leitão, P.J., Marcantonio, M., Neteler, M., Ricotta, C., Schmidtlein, S., Vihervaara, P., Wegmann, M., Nagendra, H. (2018):
Measuring β-diversity by remote sensing: A challenge for biodiversity monitoring
Methods Ecol. Evol. 9 (8), 1787 - 1798 10.1111/2041-210X.12941
2017 (5)
- Dechant, B., Cuntz, M., Vohland, M., Schulz, E., Doktor, D. (2017):
Estimation of photosynthesis traits from leaf reflectance spectra: Correlation to nitrogen content as the dominant mechanism
Remote Sens. Environ. 196 , 279 - 292 10.1016/j.rse.2017.05.019 - Lange, M., Dechant, B., Rebmann, C., Vohland, M., Cuntz, M., Doktor, D. (2017):
Validating MODIS and Sentinel-2 NDVI products at a temperate deciduous forest site using two independent ground-based sensors
Sensors 17 (8), art. 1855 10.3390/s17081855 - Padró, J.-C., Pons, X., Aragonés, D., Díaz-Delgado, R., García, D., Bustamante, J., Pesquer, L., Domingo‐Marimon, C., González-Guerrero, O., Cristóbal, J., Doktor, D., Lange, M. (2017):
Radiometric correction of simultaneously acquired Landsat-7/Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2A imagery using Pseudoinvariant Areas (PIA): Contributing to the Landsat time series legacy
Remote Sens. 9 (12), art. 1319 10.3390/rs9121319 - Schröter, I., Paasche, H., Doktor, D., Xu, X., Dietrich, P., Wollschläger, U. (2017):
Estimating soil moisture patterns with remote sensing and terrain data at the small catchment scale
Vadose Zone J. 16 (10) 10.2136/vzj2017.01.0012 - Xu, X., Conrad, C., Doktor, D. (2017):
Optimising phenological metrics extraction for different crop types in Germany using the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectrometer (MODIS)
Remote Sens. 9 (3), art. 254 10.3390/rs9030254
2016 (6)
- Carl, G., Doktor, D., Schweiger, O., Kühn, I. (2016):
Assessing relative variable importance across different spatial scales: a two-dimensional wavelet analysis
J. Biogeogr. 43 (12), 2502 - 2512 10.1111/jbi.12781 - Feilhauer, H., Doktor, D., Schmidtlein, S., Skidmore, A.K. (2016):
Mapping pollination types with remote sensing
J. Veg. Sci. 27 (5), 999 - 1011 10.1111/jvs.12421 - Gerstmann, H., Doktor, D., Gläßer, C., Möller, M. (2016):
PHASE: A geostatistical model for the Kriging-based spatial prediction of crop phenology using public phenological and climatological observations
Comput. Electron. Agric. 127 , 726 - 738 10.1016/j.compag.2016.07.032 - Lange, M., Schaber, J., Marx, A., Jäckel, G., Badeck, F.W., Seppelt, R., Doktor, D. (2016):
Simulation of forest tree species’ bud burst dates for different climate scenarios: chilling requirements and photo-period may limit bud burst advancement
Int. J. Biometeorol. 60 (11), 1711 - 1726 10.1007/s00484-016-1161-8 - Luft, L., Neumann, C., Itzerott, S., Lausch, A., Doktor, D., Freude, M., Blaum, N., Jeltsch, F. (2016):
Digital and real-habitat modeling of Hipparchia statilinus based on hyper spectral remote sensing data
Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 13 (1), 187 - 200 10.1007/s13762-015-0859-1 - Richter, R., Reu, B., Wirth, C., Doktor, D., Vohland, M. (2016):
The use of airborne hyperspectral data for tree species classification in a species-rich Central European forest area
Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 52 , 464 - 474 10.1016/j.jag.2016.07.018
2015 (2)
- Lausch, A., Salbach, C., Schmidt, A., Doktor, D., Merbach, I., Pause, M. (2015):
Deriving phenology of barley with imaging hyperspectral remote sensing
Ecol. Model. 295 , 123 - 135 10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2014.10.001 - Neumann, C., Weiss, G., Schmidtlein, S., Itzerott, S., Lausch, A., Doktor, D., Brell, M. (2015):
Gradient-based assessment of habitat quality for spectral ecosystem monitoring
Remote Sens. 7 (3), 2871 - 2898 10.3390/rs70302871
2014 (3)
- Brosinsky, A., Lausch, A., Doktor, D., Salbach, C., Merbach, I., Gwillym-Margianto, S., Pause, M. (2014):
Analysis of spectral vegetation signal characteristics as a function of soil moisture conditions using hyperspectral remote sensing
J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 42 (2), 311 - 324 10.1007/s12524-013-0298-8 - Doktor, D., Lausch, A., Spengler, D., Thurner, M. (2014):
Extraction of plant physiological status from hyperspectral signatures using machine learning methods
Remote Sens. 6 (12), 12247 - 12274 10.3390/rs61212247 - Feilhauer, H., Dahlke, C., Doktor, D., Lausch, A., Schmidtlein, S., Schulz, G., Stenzel, S. (2014):
Mapping the local variability of Natura 2000 habitats with remote sensing
Appl. Veg. Sci. 17 (4), 765 - 779 10.1111/avsc.12115
2013 (5)
- Brell, M., Rogass, C., Segl, K., Spengler, D., Kuester, T., Itzerott, S., Chabrillat, S., Roessner, S., Lausch, A., Doktor, D., Kaufmann, H. (2013):
An automated pre-processing chain for airborne hyperspectral data including radiometric calibration, atmospheric correction and direct georeferencing
Conference: 8th EARSeL SIG Imaging Spectroscopy Workshop Nantes, France
10.13140/2.1.2932.1604 - Carl, G., Doktor, D., Koslowsky, D., Kühn, I. (2013):
Phase difference analysis of temperature and vegetation phenology for beech forest: a wavelet approach
Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 27 (5), 1221 - 1230 10.1007/s00477-012-0658-x - Lausch, A., Pause, M., Doktor, D., Preidl, S., Schulz, K. (2013):
Monitoring and assessing of landscape heterogeneity at different scales
Environ. Monit. Assess. 185 (11), 9419 - 9434 10.1007/s10661-013-3262-8 - Lausch, A., Pause, M., Merbach, I., Zacharias, S., Doktor, D., Volk, M., Seppelt, R. (2013):
A new multiscale approach for monitoring vegetation using remote sensing-based indicators in laboratory, field, and landscape
Environ. Monit. Assess. 185 (2), 1215 - 1235 10.1007/s10661-012-2627-8 - Lausch, A., Zacharias, S., Dierke, C., Pause, M., Kühn, I., Doktor, D., Dietrich, P., Werban, U. (2013):
Analysis of vegetation and soil patterns using hyperspectral remote sensing, EMI, and gamma-ray measurements
Vadose Zone J. 12 (4) 10.2136/vzj2012.0217
2012 (1)
- Doktor, D., Lange, M., Koslowsky, D. (2012):
Evaluation of methods to compute green-up dates based on daily NDVI observations
2012 IEEE 32nd International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Munich, Germany, 22-27 July 2012
International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium IGARSS2012
Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), New York, NY, p. 4922 - 4925 10.1109/IGARSS.2012.6352508
2011 (1)
- Rogass, C., Spengler, D., Bochow, M., Segl, K., Lausch, A., Doktor, D., Roessner, S., Behling, R., Wetzel, H.-U., Kaufmann, H. (2011):
Reduction of radiometric miscalibration-applications to pushbroom sensors
Sensors 11 (6), 6370 - 6395 10.3390/s110606370
2009 (1)
- Doktor, D., Bondeau, A., Koslowski, D., Badeck, F.-W. (2009):
Influence of heterogeneous landscapes on computed green-up dates based on daily AVHRR NDVI observations
Remote Sens. Environ. 113 (12), 2618 - 2632 10.1016/j.rse.2009.07.020
