Research platform Middle Elbe
Project leader: Dr. Mathias Scholz

Project staff: Dr. Mathias Scholz, Dr. Holger Rupp, Hans Dieter Kasperidus, Dipl.-Geogr. Franziska Löffler, Dr. Peter Dietrich
Status: Helmholtz Centre for Environmental Research - UFZ
Interdisciplinary research platform for floodplain ecology in the Middle Elbe
A multidisciplinary research platform has been established in the UNESCO Biosphere reserve Middle Elbe as integral part of the TERENO-program. Different scientific groups inside and outside the UFZ are working together to understand floodplain ecology, functioning and management. The platform is in the continuum of the successful multidisciplinary collaboration developed within the RIVA and HABEX projects which has allowed the collection of valuable data on floodplain ecosystems since 1998. One key activity is the Rosslau experiment.

The Rosslau experiment offers the unique opportunity to follow the first implemented floodplain restoration project in the UNESCO biosphere reserve Riverine Landscape Elbe. It is assumed that reactivated floodplains will restore dynamic alluvial habitats with high biodiversity and reinforce the multiple floodplain functions. The assessment of the effects of such restoration measures requires long-term research platforms for interdisciplinary research. An integrated multidisciplinary approach was chosen to study complex floodplain dynamics and interactions between the different environmental compartments successfully.
The Rosslau experiment-an innovative study design for an interdisciplinary restoration experiment in the Elbe river floodplain
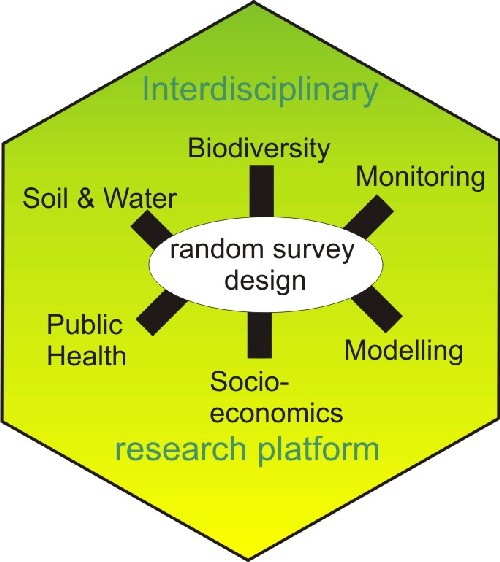
Since spring 2006, a multidisciplinary research platform is established by the UFZ to study exemplarily short-term and long-term effects of floodplain restoration on floodplain ecosystem services and functions in the Rosslau area. According to the needs to study effects of floodplain management, three different sub-areas have been chosen: restoration area, untouched active floodplain, and disconnected floodplain. The stratified, randomised study design with interdisciplinary study plots, developed and tested in the RIVA project and HABEX project sets the scientific basis to all participating disciplines and is to be considered as the core of the research platform. It enables repeated surveys of the same plots for biotic (molluscs, insects, vegetation) and abiotic (soil, nutriments, pollutants, hydrology) factors.
With more than 10 UFZ departments and external partners participating in the project, this experiment is not only a scientific monitoring program but also intends to create a science-society interface for a better management of dike relocation.
Project objectives
- Analyses of biodiversity and ecosystem services in floodplains
- Quantification of filtration, transport and buffering processes
- Test of non-invasive monitoring methods for hydrogeology studies
- Prediction of habitat function using biological and environmental factors
- Assessment of potential effects of climate change on floodplain functions and biodiversity
- Integrated approach for mosquito management in floodplains
- Evaluation of the dike relocation from a socio-economical point of view
- Transferability of the results to other floodplain sectors or river systems

Project partners
UFZ departments:
Conservation Biology
Soil Physics
Soil Chemistry
Monitoring & Exploration Technologies
Division of Social Sciences
Groundwater Remediation
Applied Landscape Ecology
System Ecotoxicology
Lake Research
External cooperations:
Biosphere Reserve Middel Elbe/Riverine Landscape Elbe
BfG - Federal Institute of Hydrology
Elena - Consulting for Soil Science, Falkenberg
HS Anhalt- Anhalt University of Applied Sciences
ILN - Institut für Landschaftsökologie und Naturschutz-Bühl
ÖKON - Ltd. Ass. for Landscape Ecology, Aquatic Biology and Environment planning
TU Berlin- Technische Universität Berlin
Bergische Univeristät Wuppertal- Abteilung Bauingenieurwesen
Further cooperation on specific topics are welcome! - Contact
