Press release, 5 November 2013
Global map provides new insights into land use
UFZ researchers show the complexity of land use by mapping its common patterns
Leipzig. In order to assess the global impacts of land use on the environment and help provide appropriate countermeasures, a group of researchers under the leadership of the Helmholtz Centre for Environmental Research (UFZ) has created a new world map of land use systems. Based on various indicators of land-use intensity, climate, environmental and socio-economic conditions, they identified twelve global patterns called land system archetypes. The scientists from UFZ with colleagues from the Humboldt-University Berlin and University Bonn have recently published their results in the journal Global Environmental Change.
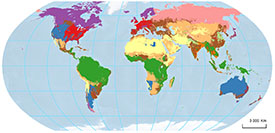
Land use changes come in various forms: maize fields replace meadows and grasslands, tropical forests are cleared for pastures, steppes become cropland. The reasons are complex, the impacts are immense: animal and plant communities change, ecosystem functions disappear, carbon emissions contribute to climate change. Whatever happens regionally has global consequences. In order to better assess these impacts and help provide effective countermeasures, the researchers from UFZ created a world map that identifies twelve global land-use systems, also called archetypes. These include barren lands in the developing world, pastoral systems or extensive cropping systems. Germany, for instance, together with most of the Western Europe, Eastern USA and Eastern Australia represents the ‘intensive cropping system’ that covers about 5% of the terrestrial Earth surface. This system is characterised by high density of cropland, high inputs of nitrogen fertilisers, temperate climate, high crop yields, large capital investments in the agricultural sector, low proportion of GDP originating from agriculture and good access to market places.
What is novel about this research is the fact that the scientists analyzed significantly more data and indicators than what is common in similar studies. In contrast to traditional models of land use, over 30 factors with more than one million data points were processed. “For example, we didn’t know before which regions had an unfulfilled potential for agricultural intensification given the environmental and socio-economic conditions, or in which regions the maximum agricultural yields were already achieved”, says Tomáš Václavík, a scientist and leading author from UFZ. The information that was usually hidden behind the complexity of data is now revealed. “If we had analysed only the environmental indicators, we could not identify where viable opportunities for yield improvements exist”.
This new analysis also shows a different picture of land use than scientists had before. China, for example, belongs to five different archetypes. “It was surprising to see that the intensity and type of land use in some regions of China was quite similar to the situation in Western Europe or the United States. Thus, parts of China, together with particular regions of India and, of course, large areas of Europe, were assigned to the ‘intensive cropping systems’ archetype”, says Tomáš Václavík.
According to the co-author and the head of the Department of Computational Landscape Ecology at UFZ Leipzig, Prof. Ralf Seppelt, this representation of land systems is useful also because we can now provide science-based policy recommendations for regions in certain land-use types on how to avoid negative consequences of land use. This can be easily explained with examples from Latin America and Southeast Asia: many areas in these regions are classified as ‘degraded forest/cropland systems in the tropics’ characterized by extremely high soil erosion. Because the socio-economic data show that agriculture plays an important role in the national economy of the local countries, it is essential to develop and apply erosion control measures for these regions. Only then the agricultural yields could increase without negatively affecting the environment. In other land systems the situation is quite different. The extensive cropping systems of Eastern Europe or India still have a high potential to increase the agricultural yields. Such opportunities, however, are largely exhausted in the intensive cropping systems of Western Europe and the USA.
This study is a product of the scientific coordination project GLUES (Global Assessment of Land Use Dynamics, Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Ecosystem Services), which is a part of the Sustainable Land Management research program funded by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research. In this program, international research teams investigate land use changes in twelve regions worldwide. The GLUES team not only links the regional projects and communicates their results to the public and the scientific community, but it also conducts research in the area of scientific synthesis as in the current study. For Ralf Seppelt, the leader of the GLUES project, the land system archetypes thus represent an important achievement: “They help us understand the interactions between human activities on the one hand and social and environmental changes on the other.”
Benjamin Haerdle/ Tilo Arnhold
Publication:
Tomáš Václavík, Sven Lautenbach, Tobias Kuemmerle, Ralf Seppelt (2013):
Mapping global land system archetypes. Global Environ. Change.This study is a part of the “Sustainable Land Management” research programme and was funded by the Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF), the European Commission and the Einstein Foundation.
Additional Information:
Prof. Ralf Seppelt
Helmholtz Centre for Environmental Research (UFZ)
Phone: +49-341-235-1250, -1952
http://www.ufz.de/index.php?en=13905
http://www.ufz.de/index.php?en=30497
or
Tilo Arnhold, Susanne Hufe (UFZ-Public Relations)
Telefon: 0341-235-1630, -1635
http://www.ufz.de/index.php?en=640
Related Links:
Funding measure “Sustainable Land Management“:
http://nachhaltiges-landmanagement.de/en/
Short videos about GLUES and the individual regional projects can be found at:
http://modul-a.nachhaltiges-landmanagement.de/en/media-centre-module-a/video-portal/
At the Helmholtz Centre for Environmental Research (UFZ) scientists are interested in the wide-ranging causes and impacts of environmental change. They conduct research on water resources, biodiversity, the impacts of climate change and adaptation strategies, environmental and biotechnologies, bioenergy, the behaviour of chemicals in the environment and their effects on health, modelling and sociological issues. Their guiding motto: our research serves the sustainable use of natural resources and helps towards long-term food and livelihood security in the face of global change. The UFZ has over 1100 employees working in Leipzig, Halle und Magdeburg. It is funded by the federal government, as well as by the State of Saxony and Saxony Anhalt.
http://www.ufz.de
The Helmholtz Association contributes to finding solutions for large and pressing issues in society, science and the economy through excellence in the following six areas of research: energy, earth and the environment, health, key technologies, structure of matter, transport and aerospace. With almost 35,000 employees and coworkers in 18 research centres and an annual budget of approx. 3.8 billion Euros the Helmholtz Association is the largest scientific organization in Germany. Work is conducted in the tradition of the renowned natural scientist Hermann von Helmholtz (1821-1894).
http://www.helmholtz.de/en