ORDIAmur – Overcoming replant disease by an integrated approach
Funding reference: 031B0025G
Ordiamur is one of the 10 joint research projects of the
BonaRes
research initiative which is funded by the Federal Ministry of Education and Research. A network of 16 interdisciplinary sub-projects is working together in Ordiamur on an integrated approach to overcome the apple replant disease (ARD).
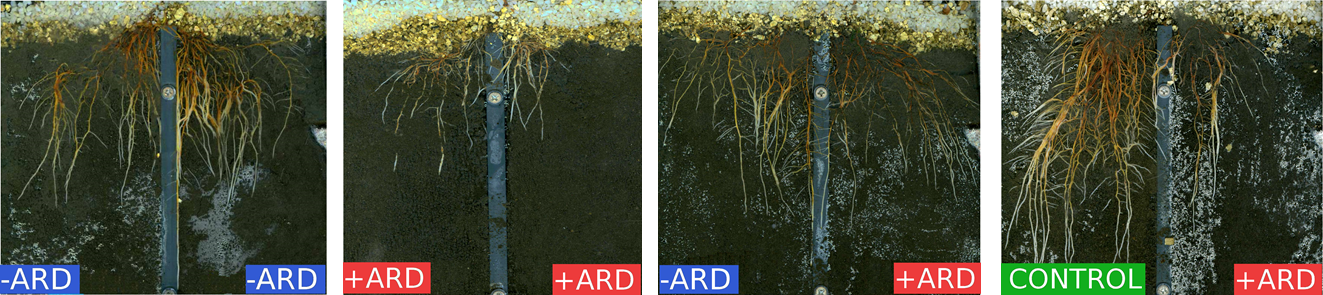
ARD occurs wherever apples have been planted in at least the second generation, especially in nurseries and apple orchards. Symptoms of ARD include reduced tree growth and a decline in crop yields. One assumption to explain this phenomenon is that through soil cultivation spatial organization/differentiation created by previous crops is lost and hence new roots cannot grow in favorable sites or avoid unfavorable sites. Unfavorable conditions could be high toxin concentrations, signaling substances or high number and abundance of pathogens. Avoiding ARD through crop rotation is not feasible. Likewise soil sterilization and fumigation are no satisfactory alternatives for the control of ARD. Soil sterilization requires great effort, making it almost impractical in economically used apple stocks. Furthermore soil disinfectants are ecologically harmful and also forbidden in Germany. Hence, the development of alternative approaches for handling ARD is needed to maintain a sustainable soil productivity. The aim of our work is to detect the spatial distribution of possible ARD causing agents both in the bulk soil and in the rhizosphere. X-ray computer tomography (CT) is an eligible tool for non-destructive imaging of root systems and their development over time. After CT scanning, the observed root growth can be related to distribution of ARD affected soil and conclusions can be drawn regarding ARD causing factors, their spatial distribution and mobility in soil.
Further focal points in Ordiamur are the analysis of root exudates and the microbiome in the rhizosphere, sequencing of microorganisms, detection of the plant reaction to infected soil and the analysis of the behavior of different genotypes in relation to ARD. These results, coupled with the findings of problem-oriented socio-economic analyses, will later be used as a basis for the development of sustainable and economic solution strategies.
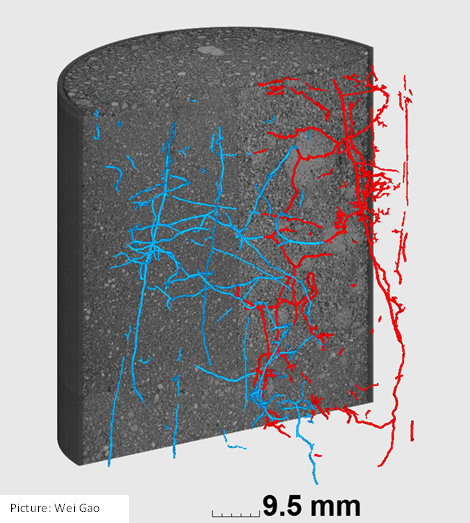
Left: blue roots are grown in control soil,
Right: red roots are grown in ARD infected soil
Cooperation partners:
- Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz Universität Hannover
- Helmholtz-Zentrum München GmbH
- Helmholtz-Zentrum für Umweltforschung
- Hochschule Bonn-Rhein-Sieg
- Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin
- Julius Kühn-Institut
- Landwirtschaftskammer Schleswig-Holstein
- Leibniz-Zentrum für Agrarlandschaftsforschung e. V.
- Rheinische Friedrich-Wilhelms-Universität Bonn
- Technische Universität Dortmund, Rektorat / Hochschulverwaltung
- Zentrum für Betriebswirtschaft im Gartenbau e. V.
