Press Release, 10. April 2019
How much nature is lost due to higher yields?
UFZ study reveals link between increasing yields and biodiversity
The exploitation of farmland is being intensified with a focus to raising yields. The degree to which yields actually increase as a result and the extent of the simultaneous loss of biological diversity have to date been under-researched factors. An international team of scientists led by the UFZ has now evaluated data from worldwide research in which both yield and biodiversity were examined before and after intensification measures. The findings of this meta-analysis have now been published in the journal Global Change Biology.
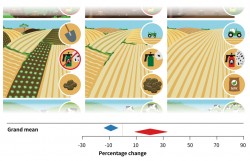
Photo: UFZ
Around 80 percent of land area in Europe is used for settlement, agriculture and forestry. In order to increase yields even further than current levels, exploitation is being intensified. Areas are being consolidated in order to cultivate them more efficiently using larger machines. Pesticides and fertilisers are increasingly being used and a larger number of animals being kept on grazing land. "Such measures increase yield but, overall, they also have negative impacts on biodiversity," says UFZ biologist Dr. Michael Beckmann. "This is because even agricultural areas offer fauna and flora a valuable habitat - which is something that is frequently not sufficiently taken into consideration." In addition, previous studies have mostly examined the effects of intensified land use only from one perspective: either with regard to the increase in yield or the loss of biodiversity. "We unfortunately still know far too little about the relationship between the two and what price nature ultimately has to pay for increases in yield," says Beckmann. In the recent study, the team of scientists aimed to address this knowledge gap.
To this end, the researchers sifted through some 10,000 topically relevant studies looking for those that collected measurement data for yield and biodiversity both before and after intensification measures. "The majority of the studies fell through the net in this respect. A mere 115 studies actually measured both parameters for the same areas, making them relevant for our purposes," says Beckmann. The 449 agricultural areas examined in these studies are, however, distributed around the globe, are located in different climatic zones and the time they have been in use varies greatly. To be able to use these studies for their analysis, the researchers developed a mathematical model that takes account of these differences and renders the data comparable. They then summarised the respective yield increases and biodiversity losses. "We were able to demonstrate that, on average, intensification of land use gave rise to an increase in yield of 20 percent but this is, at the same time, associated with a nine percent loss of species," says Beckmann.
To obtain a more detailed insight into the impact of intensification measures, the researchers divided the agricultural areas into three classes of intensity - low, medium and high. Proceeding in this way made it possible to compare the results of all three agricultural production systems - arable land, grasslands and forest - with each other. Areas of medium intensity of use demonstrated the highest increase (85 percent) in yield following intensification measures. But they also had the greatest loss of species (23 percent). In contrast, areas that already had high intensity of use did not reveal any significant loss of species but still showed an increase in yield of 15 percent. "Initially, this sounds excellent: greater yield without loss of species," says Beckmann. "But where there was not much biodiversity left to start with due to highly intense usage, there is, of course, also not much that can be lost. In such cases, the critical point may have already been passed." In a comparison of the effects of intensification measures on arable land, grasslands and forests, forests performed best with regard to lower species loss. The study findings indicate that intensified land use may, in individual cases such as timber production, also lead to greater yields without any detrimental effect on biodiversity.
The study makes clear how great the impact of the intensity of agricultural production can be for the protection of biodiversity. It reveals general trends and identifies gaps in our knowledge. Concrete recommendations for action in specific regions cannot be derived from the study, however. "Further research is necessary in order to understand the conditions under which land usage is linked to a low or an especially high risk to biodiversity," says Michael Beckmann. "This is the only way to ensure that we are able to apply intense land use practices and protect biodiversity at the same time. After all, species conservation can and must also take place in our cultivated landscapes."
This work was supported by the National Socio?Environmental Synthesis Center (SESYNC; NSF DBI?1052875) and sDiv, the Synthesis Centre of the German Centre for Integrative Biodiversity Research (iDiv) Halle?Jena?Leipzig (DFG FZT 118).
Publication:
Beckmann, M. et al.: Conventional land-use intensification reduces species richness and increases production: A global meta-analysis; Global Change Biology (2019) http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/gcb.14606
Further information
Dr Michael Beckmann
UFZ Department of Landscape Ecology
michael.beckmann@ufz.de
UFZ press office
Susanne Hufe
Phone: +49 341 6025-1630
presse@ufz.de
In the Helmholtz Centre for Environmental Research (UFZ), scientists conduct research into the causes and consequences of far-reaching environmental changes. Their areas of study cover water resources, ecosystems of the future, environmental technologies and biotechnologies, the effects of chemicals in the environment, modelling and social-scientific issues. The UFZ employs more than 1,100 staff at its sites in Leipzig, Halle and Magdeburg. It is funded by the Federal Government, Saxony and Saxony-Anhalt.
www.ufz.deThe Helmholtz Association contributes to solving major challenges facing society, science and the economy with top scientific achievements in six research fields: Energy; Earth and Environment; Health; Key Technologies; Matter; and Aeronautics, Space and Transport. With some 39,000 employees in 19 research centres, the Helmholtz Association is Germany’s largest scientific organisation.
www.helmholtz.de