Methods
Our research uses a wide range of methods, from the laboratory to the field, from the individual to the community level, as real or modelled systems.

Biotests
Laboratory systems, test organism: Daphnia magna (e.g. OECD 202, OECD 211) and Culex pipiens (mosquito larvae).

Nanocosms
Laboratory systems, automated monitoring of populations and simple communities by image analysis, Daphnia magna und Culex pipiens, test volume of 5 l.
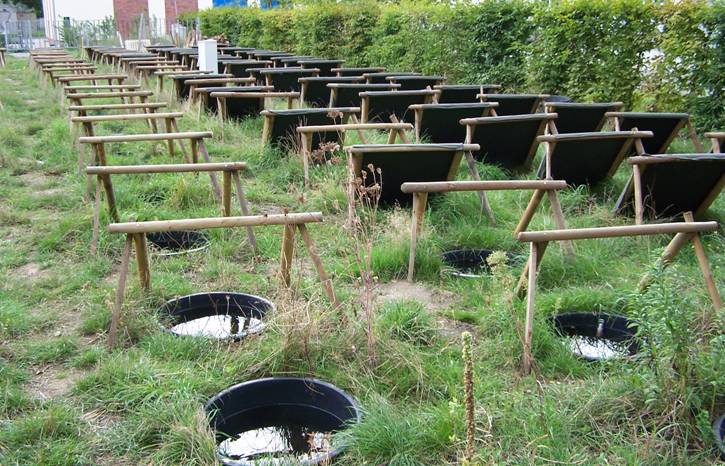

Microcosms
UFZ area, zooplankton, volume of 20-90 l, 200 replicates.
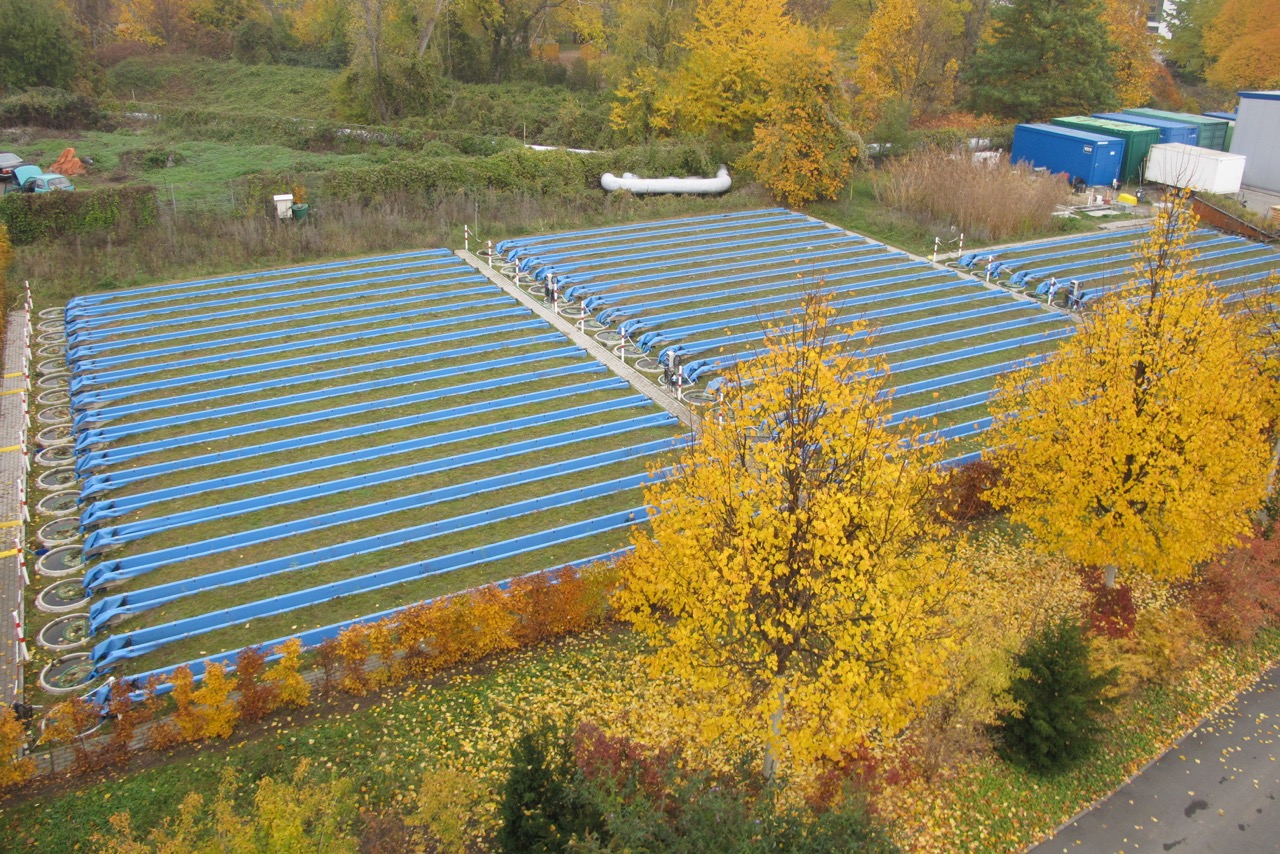

Stream Experiment Leipzig
UFZ area, macrozoobenthos, length of 14 m, 47 replicates in continuous operation, closed water circuit.

Field investigations
Measurement campaigns, monitoring of macroinvertebrates and toxic exposure, water and sediment sampling, continuous and event-triggered sample techniques.

SPEAR (Species at Risk)
Toxic specific bioindicator for running waters, based on macroinvertebrates and their ecological traits.
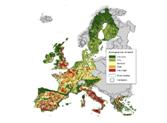
GIS-Modelling
Modelling of pesticide exposure and ecological risk in agricultural landscapes, risk maps, scenarios of global change.
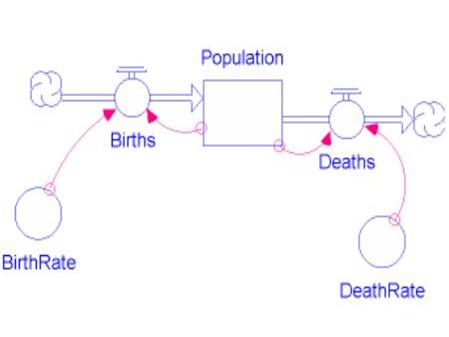
Ecological modelling
Population- and community level, toxic effects and recovery considering ecological mechanisms like competition and predation.
