Work Package A: Urban water management

December 2017
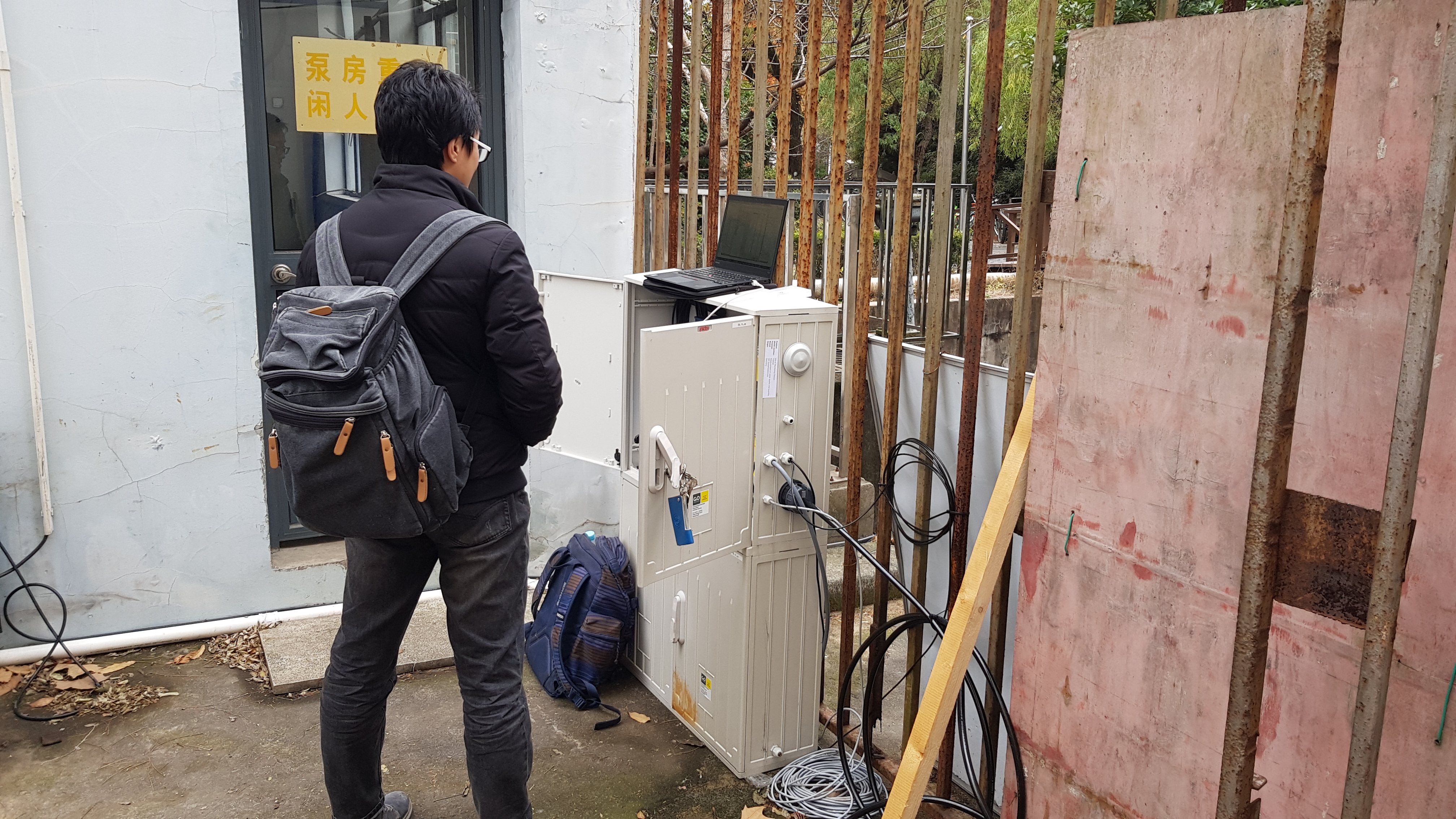
After successful clarification of customs procedures and transport requirements, the monitoring stations for the online measurement of water quality and quantity parameters arrived at the campus of Tongji University in Shanghai in December. Together with Prof. LIAO and his students each of the four stations was unpacked and every sensor was connected. One of the most important parts was to show and explain all necessary steps for calibration of the different probes. In order to establish a certain routine in dealing with online monitoring equipment, one of the stations was taken to a pumping station on campus and the sensors were installed. The pumping station is supplied by waste water from the surrounding student dormitories and university buildings as well as rain water from the campus. When the reservoir in front of the pump is filled to a certain extent, the pump starts pumping water into the Shanghai sewer system. The graphs below show three different parameters for two days in December. The water level rises steadily and falls very quickly when the pump starts to empty the reservoir. The concentration of NH4-N correlates with the usual human water consumption pattern. Especially in the morning it is up to four times higher than the average, which is very common in urban sewer networks. Since raw data is displayed, it can be seen that the electrical conductivity values drop very briefly when the reservoir is almost empty and the probe is in the air. Considering this, the graph (Fig 1) correlates to the NH4¬-N concentration as this contributes to the conductivity of a water.
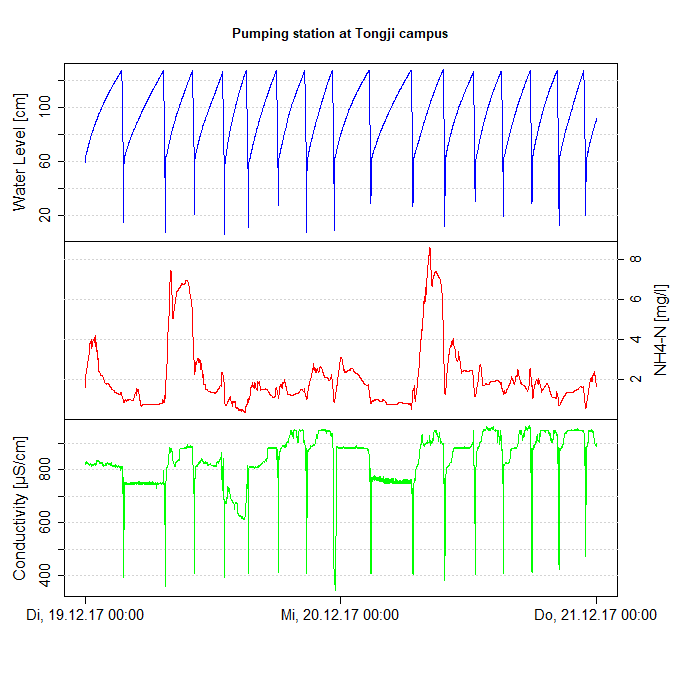
Fig 1: Pumping station at Tongji campus
The system will run at the pumping station until March and will be used as a training object for the Chinese students. During this time, the spectroscopy sensor will be calibrated to observe parameters like COD, NO3-N or turbidity. The sensors of all other stations have been calibrated in the laboratory of Tongji University and are ready to be installed. The planned remote data transmission has also almost been set up. The stability of the internet connection is currently being worked on to ensure a robust and durable data transmission. In spring the monitoring stations will be brought to the Chaohu model region to observe real data.




August 2017
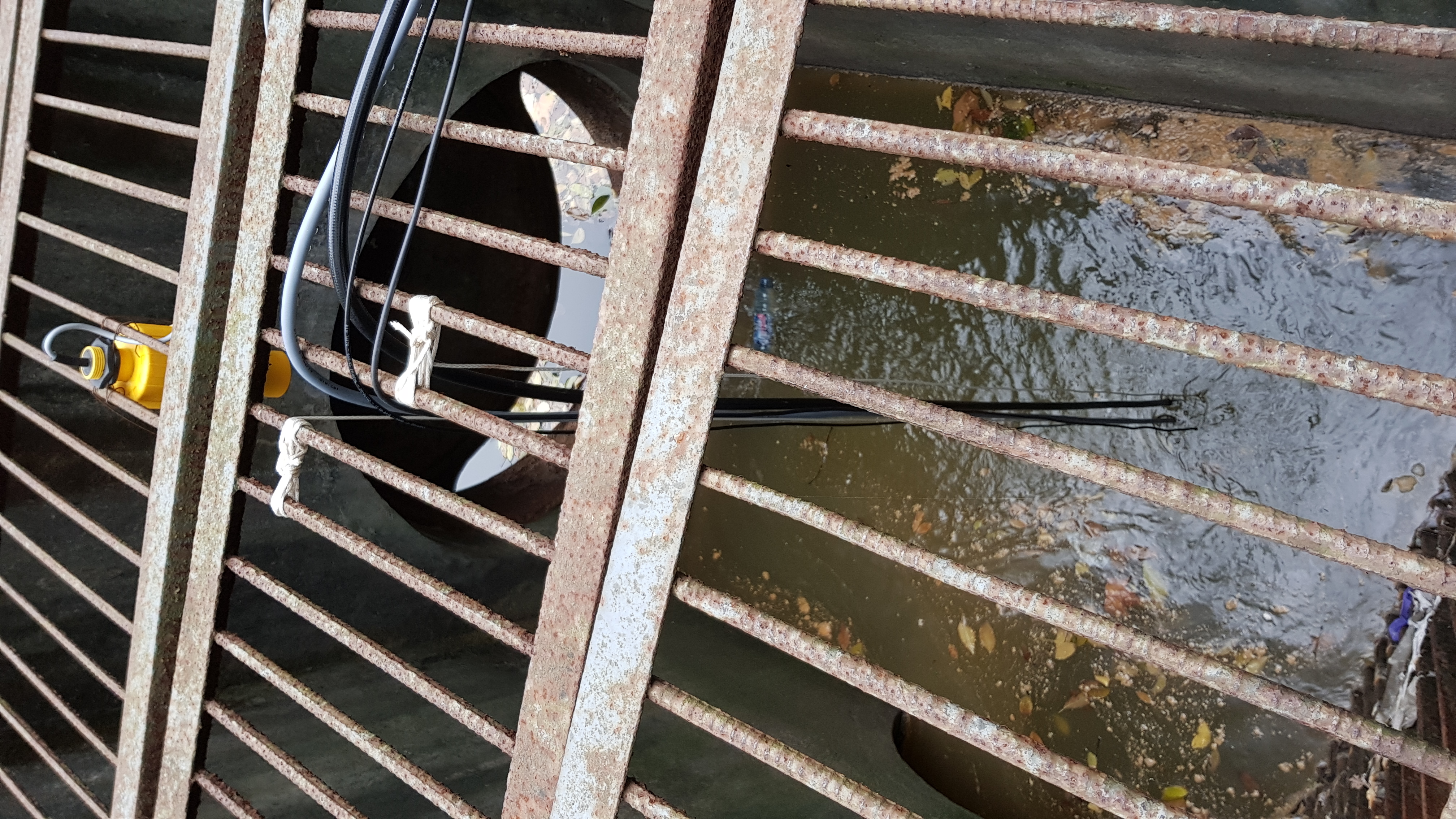
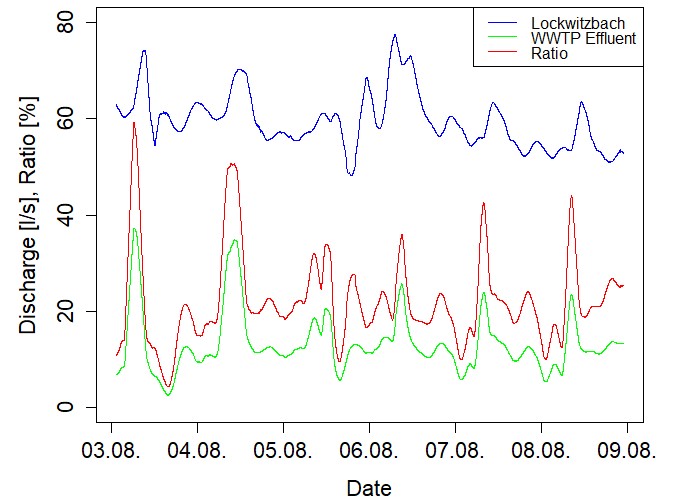
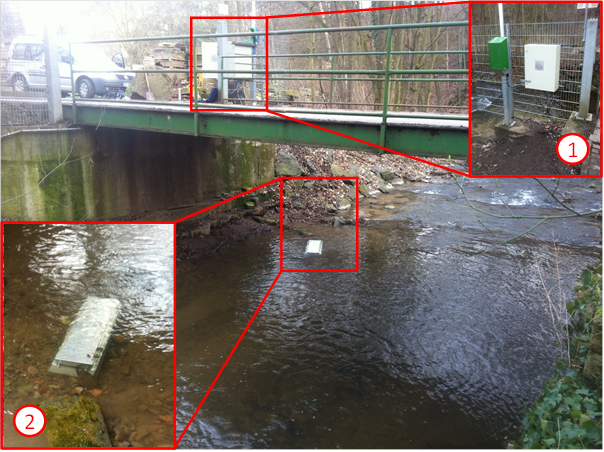
During July and August, the monitoring stations for Chaohu City were tested intensively at Lockwitzbach creek near Dresden. The set consists of four different stations for measuring various physical and chemical parameters in sewer systems and small rivers. One station designed for operation at a sewer was installed at the effluent of the waste water treatment plant Kreischa, which discharges into the nearby Lockwitzbach creek. With this, parameters such as the concentration of ammonium, the electric conductivity and the water level can be observed in a high resolution. From the last one, the discharge was computed and later compared to the discharge measured about 800 m downstream of the disposal to the creek. This second station, which was installed directly at the river bank, is able to observe water level and flow velocity. After setting up a river profile, it can compute the discharge of the creek instantly and with good precision. Besides the concentration of ammonium, it is also possible to monitor the oxygen amount and the phosphorus concentration, which takes some effort to detect.
The test of both types of monitoring stations was very important for upcoming operation at Chinese rivers and sewers. For example, the wireless connection to a data server and possibilities of a remote access could be proven. Also some calibration procedures were practised.
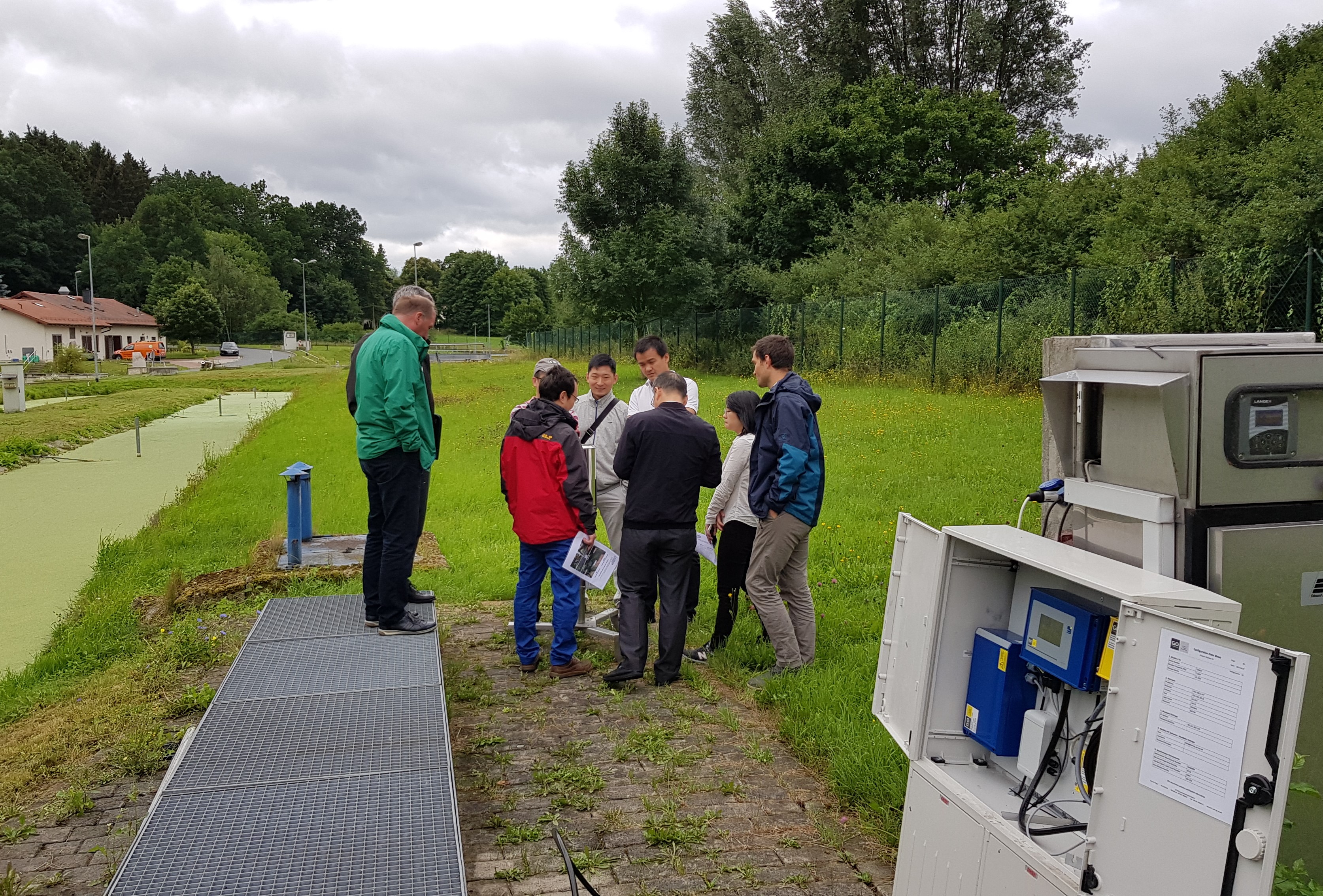
On 25th of July some of the intended Chinese operators got in a first contact with the monitoring system during their visit of different Urban catchment partners. It was shown how the stations work and what is possible to do with. After indication of different data correlation possibilities, the delegation is looking forward to the arrival and start-up of the system in China.

June 2017
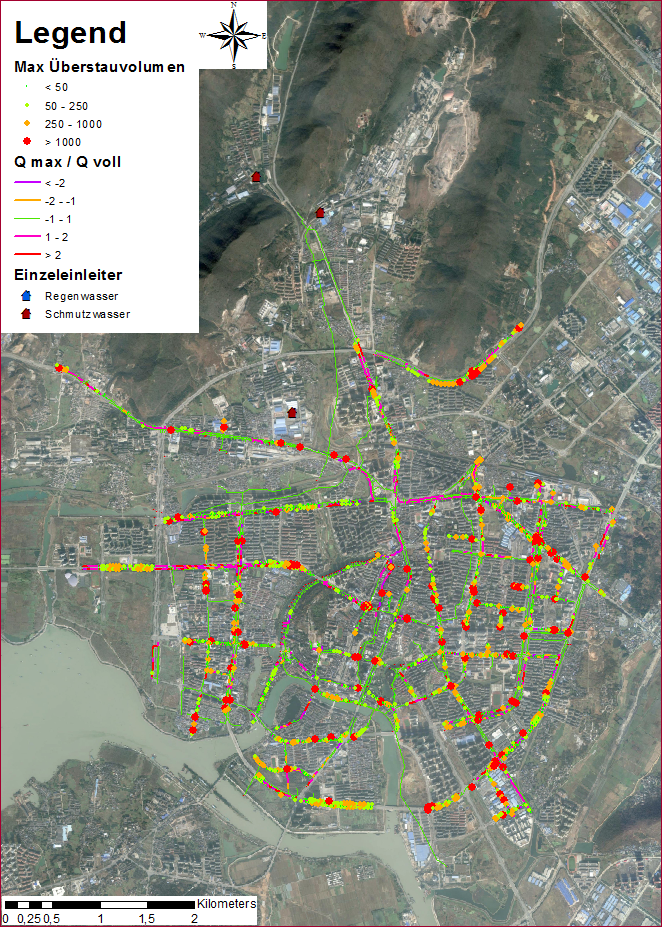
After the elimination of channelization errors, areas were assigned to the pipelines. Figure above shows the first result of hydraulic simulation under the condition of 2a heavy rainfall with the help of Hystem-Extran software (itwh). Overflow follows the punctuate distribution.
April 2017
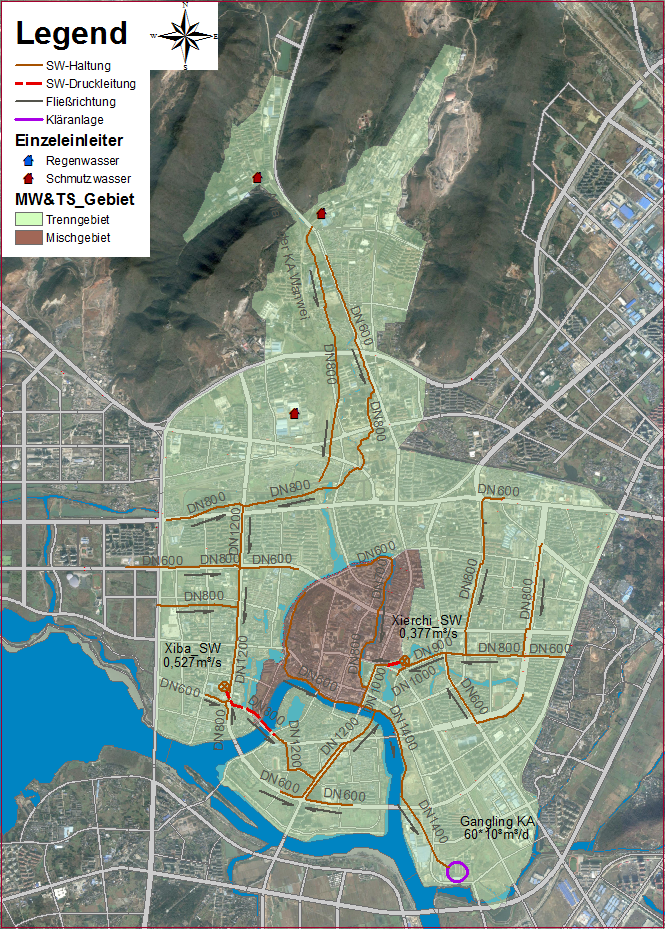
Based on the analysis of sewer data, nearly 92% channelized area is separate sewer system. Combined sewer system exists only in the old city centre, interception channel has been already constructed along the bank of moat. Main wastewater sewers are illustrated in the figure, wastewater is pumped to the wastewater treatment plant with the help of two wastewater pumping stations.
December 2016


Under the Cooperation Framework Agreement with Chinese partners, itwh offered specialized courses of Hystem-Extran and FOG in Chinese to increase the modelling level of one of our Chinese partners (Tongji University).
November 2016
1st results of the preliminary model
Based on the high-resolution digital surface model the river basin of the Shuangqiao He was determined. Statistic and deterministic algorithms were applied to preprocess the elevation model in order to remove artefacts, fill sinks, define the stream links and differentiate the subcatchments. A hydrodynamic rainfall-runoff model was implemented in EPA SWMM software. Currently plausible ranges of input parameters are investigated as a starting point for uncertainty analysis and model calibration.
August 2016
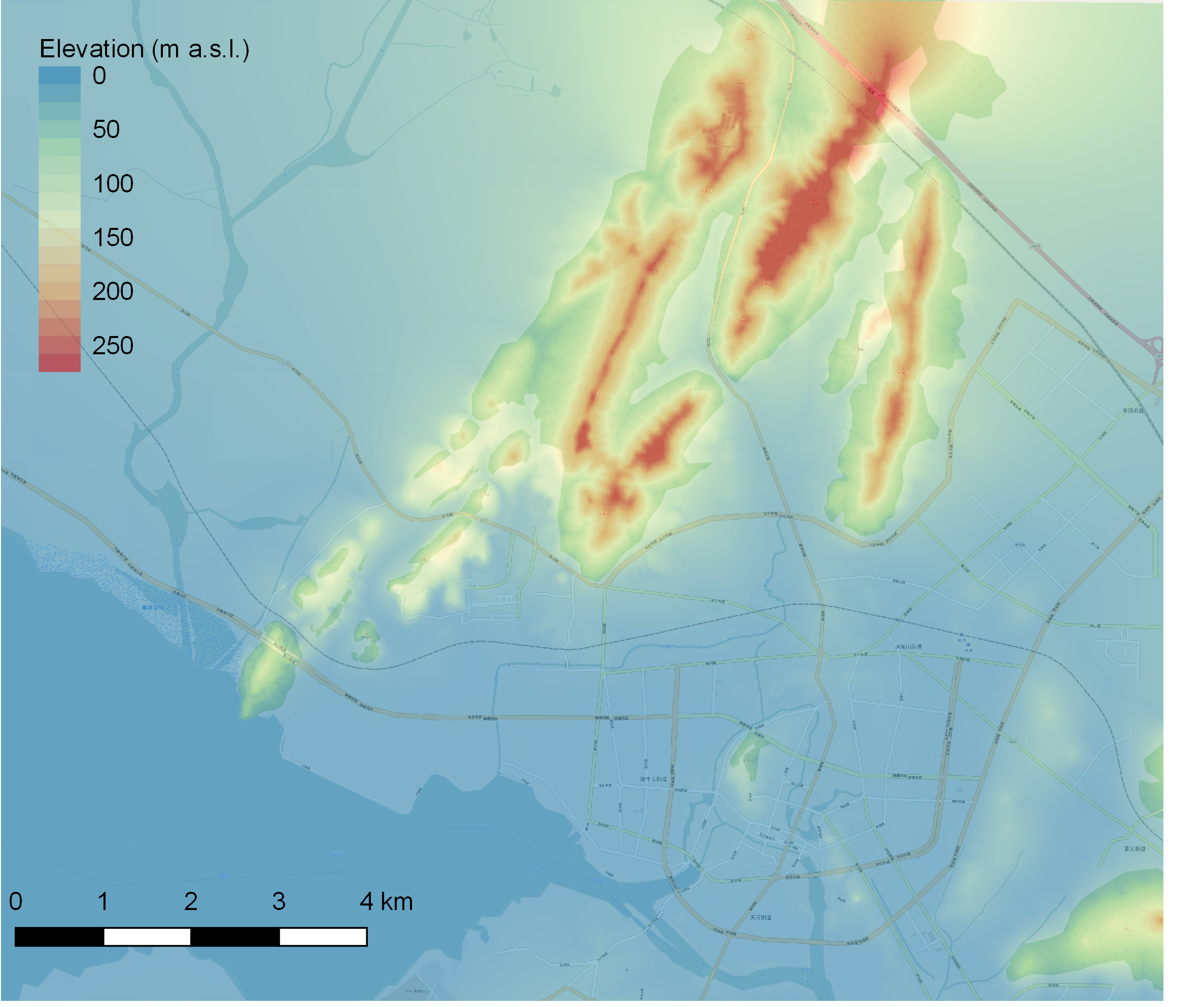
A high-resolution digital surface model, with a grid size of 4m², was generated from multiple input data sources, including a topographic map at 1:25000 scale, data on water body geometry and aerial images. It covers the area of Chaohu city center and Shuagqiao He catchment. The surface model serves as input information of rainfall-runoff modelling, hydraulic modelling of sewer and river catchment and urban flood modelling.
February 2016

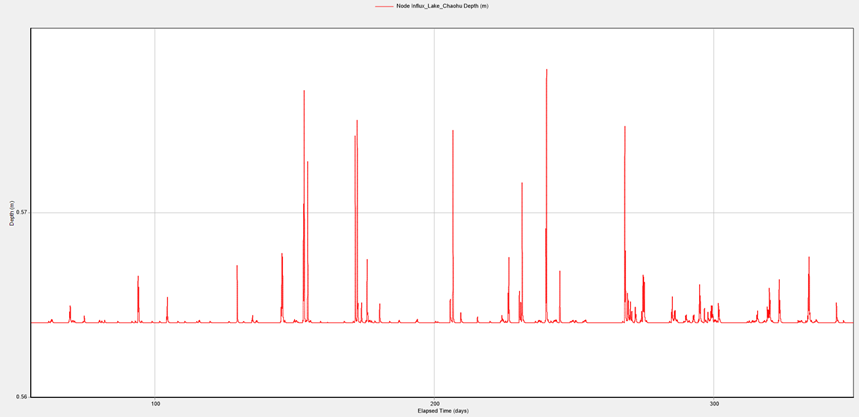
On March 22, a measuring buoy, provided through a cooperation between the UFZ and their partner Chinese institute NIGLAS, was successfully anchored on Chao Lake and began operation by two German companies, and . The following figure shows the transmitted data while the buoy was being tested ashore at the NIGLAS Institute.
During the setup of our software, technical support was provided by our cooperating partner HCSystem who provides the server technology in Shanghai. On April 21, everything was in place, and using the deployed software AL.VIS/Timeseries, the measurement data was able to be collected and used by the Chinese buoy operators. The software SensoMaster, which transmits the measured data to the database server in a uniform protocol, is used for the data transmission from the buoy to the server and the software.
Currently, about 40 series of buoy measurements are being transmitted, and the addition of more sensors to the information system is planned for measurements in flowing waters. A start has been made on a standardized procedure, developed within this project, integrating online measuring technology into the environmental information system.





