Influence of ncRNA on protein expression in cells of the immune system
For the regulation of cell processes in higher organisms like mammals, a complex machinery consisting of DNA, RNA and proteins is needed for the cell to work ‘properly’. For the last ten years it became evident that beside the normal mRNA transcripts there are RNA molecules present that do not code for a protein but exert crucial functions in terms of regulation. These molecules are called noncoding (nc) RNAs which can further be divided into subclasses of microRNAs (miRNA), small interfering RNAs (siRNA), small RNAs and medium and large RNAs.
These ncRNAs are important players in the regulation of the protein expression. They do not only regulate the mRNA translation, but also take over different functions in the regulome and interactome.
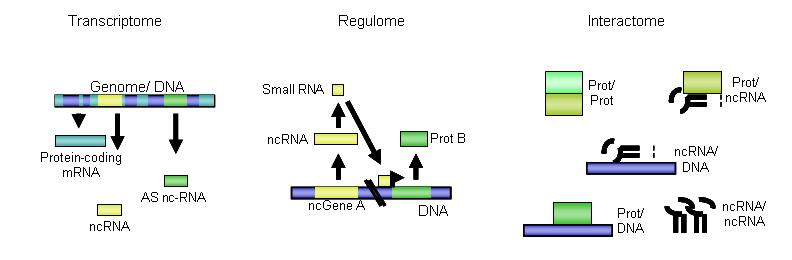
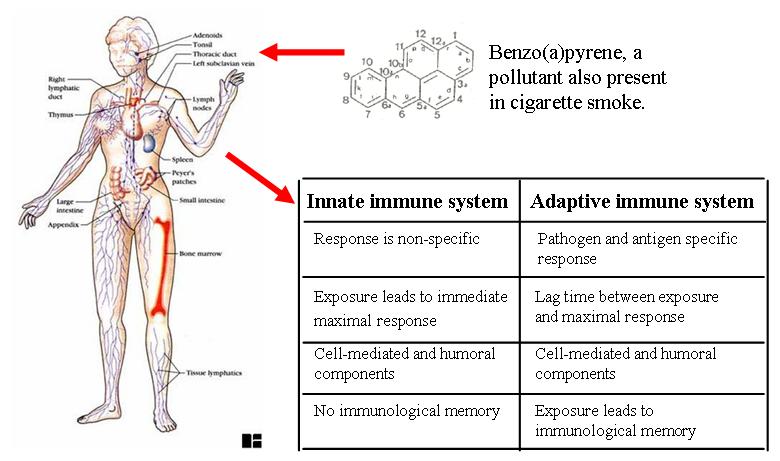
There is emerging evidence that ncRNAs also play a major role in the regulation of differentiation and functions of immune cells. Immune cells defend the body against extracellular or intracellular pathogens, diseases and cancer via the humoral or the cell-mediated immune response. In a time where environmental pollutants are a widely discussed topic, also the function of the immune system gains importance, as these pollutants have been shown to affect the immune system even at low concentrations. It has been found that pollutants, like Benzo(a)pyrene for example, higher the risk of allergic reactions.
To examine the largely unknown effects of ncRNAs, specifically miRNAs, on global protein expression in immune cells different proteomic techniques will be applied. A special focus hereby will be laid on the influence of environmental pollutants. Global and targeted proteome analysis will be carried out using gel based (DIGE), LC-MS based (SILAC) and multiple reaction monitoring (mrm) approaches.
