press release, 14. December 2016
Gene transfer on the fungal highway
UFZ researchers show how fungi can improve the genetic makeup of bacteria and their potential for the breakdown of harmful substances
Soil bacteria use the extensively branched, thread-like structures of fungi to move around and access new food sources. In a new study published in the journal Scientific Reports, UFZ researchers have been able to demonstrate that these so-called fungal hyphae also form a hot spot for gene transfer between bacteria. In this way, fungi ensure high bacterial diversity in the soil – which can also be beneficial for the degradation of pollutants.

Photo: Berthold et al. 2016 in Scientific Reports
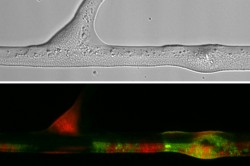
Photo: Berthold et al. 2016 in Scientific Reports
For bacteria, soil is difficult terrain, with dry areas and air spaces presenting insurmountable obstacles. In order to get around, they need a liquid film in which to swim. They don’t demand much: the mucous layer surrounding fungal hyphae is all they need to be able to move around - and they take advantage of it. The fungal network (mycelium) also provides bacteria with an excellent infrastructure: there may be hundreds of metres of fungal hyphae winding through just one gram of soil. "In the fine liquid film surrounding the hyphae, bacteria can move with much greater speed and direction and cover more distance than in soil water without hyphae," says Tom Berthold, first author of the study and a doctoral researcher at the UFZ Department of Environmental Microbiology. "For bacteria, fungal hyphae are like a motorway which gives them fast, direct access to their food sources."
Because there is often a lot of traffic on the 'fungal highway’, the bacteria may come into close contact with one another, exchanging genetic material in the process. "It’s similar to the transmission of cold germs on a packed train," explains environmental microbiologist Dr. Lukas Y. Wick. "But unlike a cold, the new genes are usually an asset to the soil bacteria. They enable them to adapt better to different environmental conditions." Depending on the genes they receive through horizontal gene transfer, they may be able to adapt to new environmental conditions or access food sources which they were previously unable to exploit. For example, this might include the pollutants toluene or benzene contained in oil and gasoline, which to bacteria with the right genetic makeup are not only not harmful but actually very tasty food. So the passing on of this ability to other bacterial groups can be very advantageous in terms of the degradation of soil pollutants.
In their research, the UFZ scientists were also able to show that much greater gene transfer takes place between bacteria on the fungal highway than in a moist environment without fungal hyphae. Using computer models that calculate the frequency of gene transfer between bacteria on the hyphae, the researchers came to the same result. Wick continues: "Our study shows that fungal hyphae not only provide soil bacteria with an excellent infrastructure, but also a potential hot spot for bacterial horizontal gene transfer. This previously unknown aspect of fungus-bacteria interaction is an important step towards understanding the complex interactions between soil-dwelling microorganisms."
Fungi therefore may play a very important role in the highly complex soil habitat: in the spread of soil bacteria, their genetic adaptation and diversity, and ultimately also their evolution. "Just a few years ago, we were still completely unaware of this," says Wick. "It's possible that over the course of the Earth’s history, bacterial diversity increased massively with the development of mycelium-forming fungi." As far as the breakdown of pollutants is concerned, the UFZ researchers conjecture that soils containing a lot of fungi are probably better equipped than soils with few fungi. This is because the fungal highway enables pollutant-degrading bacteria to reach their food faster and, with the help of gene transfer, they may even be upgraded along the way.
Publication:
Berthold T, Centler F, Hübschmann Th, Remer R, Thullner M, Harms H, Wick L. Mycelia as a focal point for horizontal gene transfer among soil Bacteria. Scientific Reports. DOI:10.1038/srep36390 http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/srep36390
Useful link:
Video "Bacteria on the 'Fungal Highway': Pseudomonas putida moving along hyphae of Cunninghamella elegans": https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AnsYh6511Ic
Further information
Dr. Lukas Wick
UFZ Department of Environmental Microbiology
Phone: +49 341 235-1316
lukas.wick@ufz.de
UFZ press office
Susanne Hufe
Phone: +49 341 235-1630
presse@ufz.de
In the Helmholtz Centre for Environmental Research (UFZ), scientists conduct research into the causes and consequences of far-reaching environmental changes. Their areas of study cover water resources, ecosystems of the future, environmental technologies and biotechnologies, the effects of chemicals in the environment, modelling and social-scientific issues. The UFZ employs more than 1,100 staff at its sites in Leipzig, Halle and Magdeburg. It is funded by the Federal Government, Saxony and Saxony-Anhalt.
www.ufz.deThe Helmholtz Association contributes to solving major challenges facing society, science and the economy with top scientific achievements in six research fields: Energy; Earth and Environment; Health; Key Technologies; Matter; and Aeronautics, Space and Transport. With some 39,000 employees in 19 research centres, the Helmholtz Association is Germany’s largest scientific organisation.
www.helmholtz.de